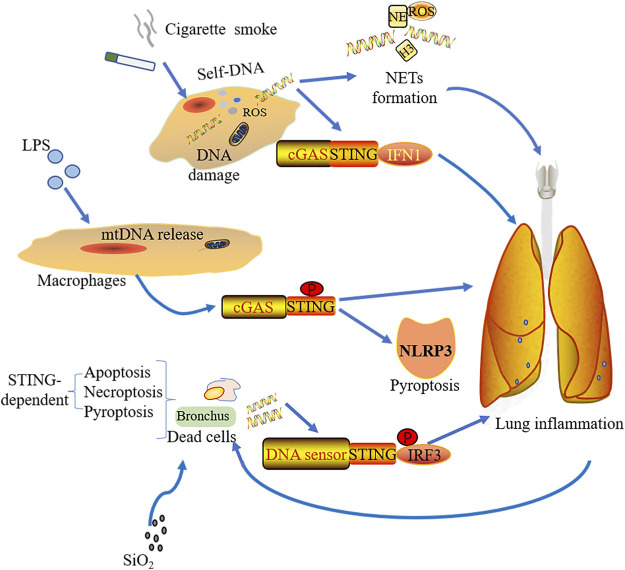
FIGURE 3.
Stimulations from various sources induce pulmonary inflammation through the cGAS-STING pathway. Cigarette smoke mediates lung inflammation by the activation of cGAS-STING-IFN1 and the formation of NETs. With simulations of LPS, macrophage could release mtDNA, which was sensed by cGAS-STING and induced NLRP3-mediated pyroptosis as well as lung inflammation. Silica exposure to bronchus leads to different forms of STING-dependent cell death including apoptosis, necroptosis, and pyroptosis. The dsDNA from the dead cells triggers lung inflammation via STING-IRF3 signaling.