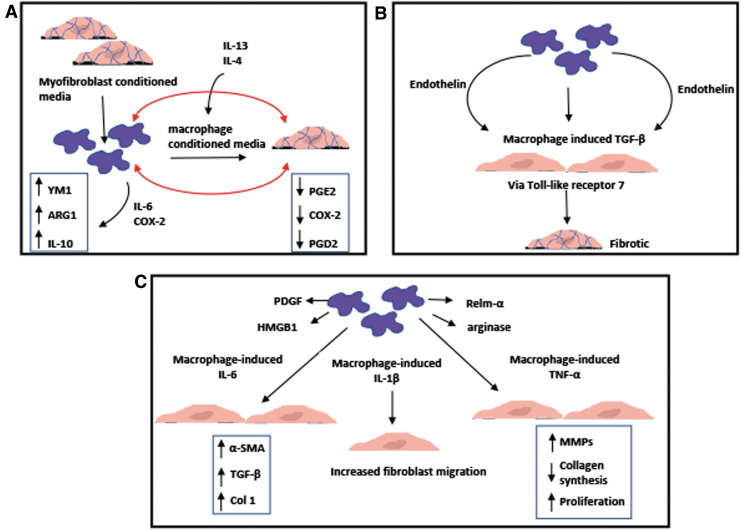
FIG. 4.
Schematics of in vitro studies demonstrating the interaction between macrophages and cardiac fibroblasts/myofibroblasts: (A) Bidirectional crosstalk through IL-6, PGE2, and PGD2 between myofibroblasts and macrophages enhanced anti-inflammatory phenotype in both cells.52 (B) Macrophages activated by immune complexes induced cardiac fibroblasts to secrete TGF-β in an endothelin-1-dependent manner through TLR7 leading to a fibrosing phenotype.56 (C) Macrophage-secreted IL-1β induced significant increase in migration of cardiac fibroblasts.56 Macrophages increased expression of α-SMA and collagen type I and production of TGF-β in cardiac fibroblasts through IL-6 signaling.57 Macrophage-induced TNF-α enhances proliferation of cardiac fibroblasts, collagen degradation, MMP activity, and inflammatory cytokine production.58 PDGF, platelet-derived growth factor; TLR7, toll-like receptor 7.