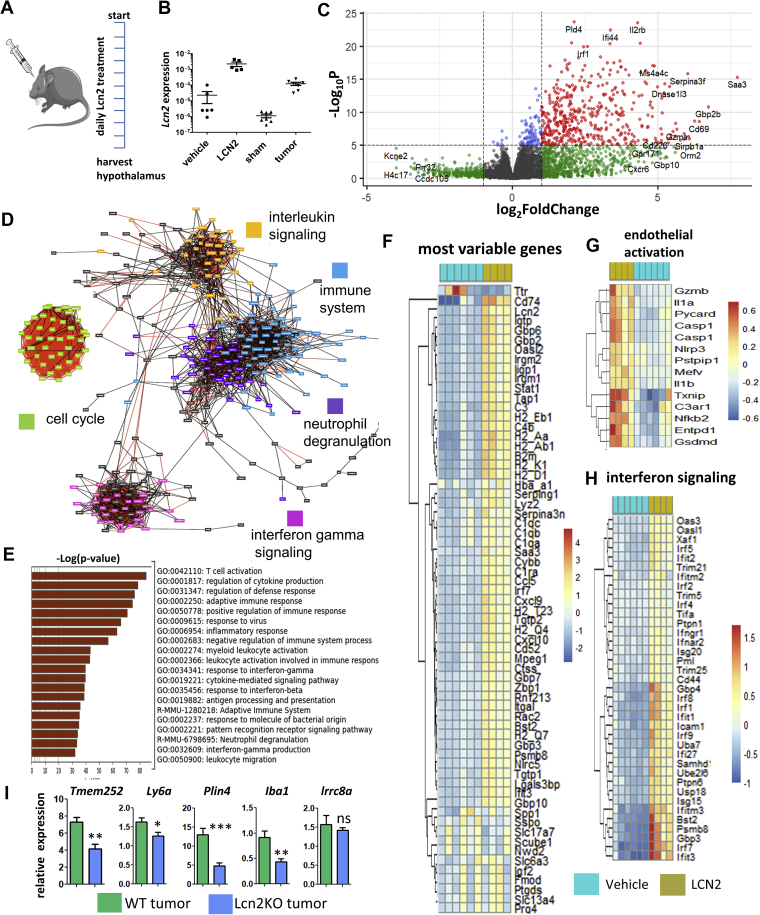
Figure 5.
LCN2 treatment induces an immune response in the hypothalamus. Treatment schedule of mice receiving LCN2 or vehicle every morning through a lateral ventricle cannula for 10 days (A). Expression of Lcn2 in LCN2-treated mice was confirmed with qPCR and compared with sham and TB mice (B). Differential gene expression assessed by RNA-seq in the hypothalamus of LCN2 or vehicle-treated mice as shown with a volcano plot (C). Main gene expression networks activated after LCN2 treatment as found by RNA-seq using the top-induced genes (D). Pathway analysis performed on genes with increased expression after LCN2 treatment, as analyzed with metascape on the top 1000 induced genes from the RNA-seq (E). Top-65 variable genes after LCN2 treatment as shown with a heatmap (F). Heatmap for genes involved in endothelial activation (G) and interferon signaling (H) after LCN2 treatment as found by RNA-Seq. qPCR analysis of cachexia markers for WT and Lcn2 KO TB mice (I). qPCR values represent the mean ± SEM of at least three independent experiments and statistical significance between groups was determined with a Student's t-test (∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗∗∗P < 0.001).