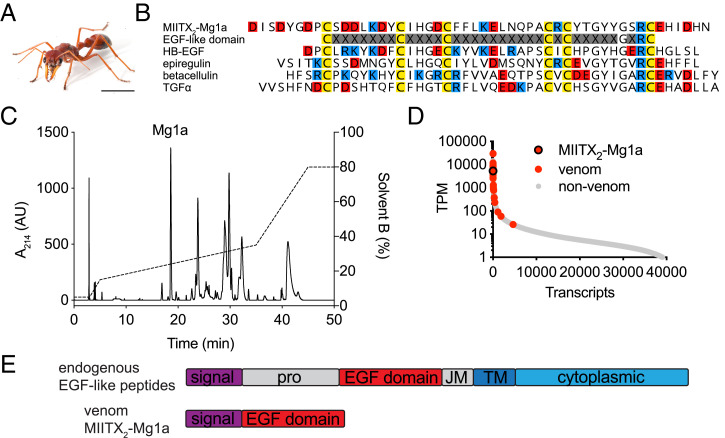
Fig. 1.
Mg1a is a major component of M. gulosa venom. (A) The Australian giant red bull ant M. gulosa. (Scale bar, 5 mm.) (B) Alignment of the sequence of Mg1a with a consensus EGF-like domain and several EGF-like peptide hormones: human HBEGF (UniProt accession no. Q99075), epiregulin (UniProt accession no. O14944), betacellulin (UniProt accession no. P35070), and TGFα (UniProt accession no. P01135). Cys, Glu/Asp, and Arg/Lys residues are colored yellow, red, and blue, respectively. (C) An RP-HPLC chromatogram of M. gulosa venom. The peak corresponding to Mg1a (as determined by MS) is labeled. AU, arbitrary units. (D) The Mg1a-encoding transcript is found in the highly expressed portion of the venom-apparatus transcriptome with an estimated expression level like that of other venom peptides (highlighted in red). (E) The prepropeptide structures of endogenous EGF-like peptide hormones and Mg1a. JM, juxtamembrane domain; pro, propeptide; TM, transmembrane domain.