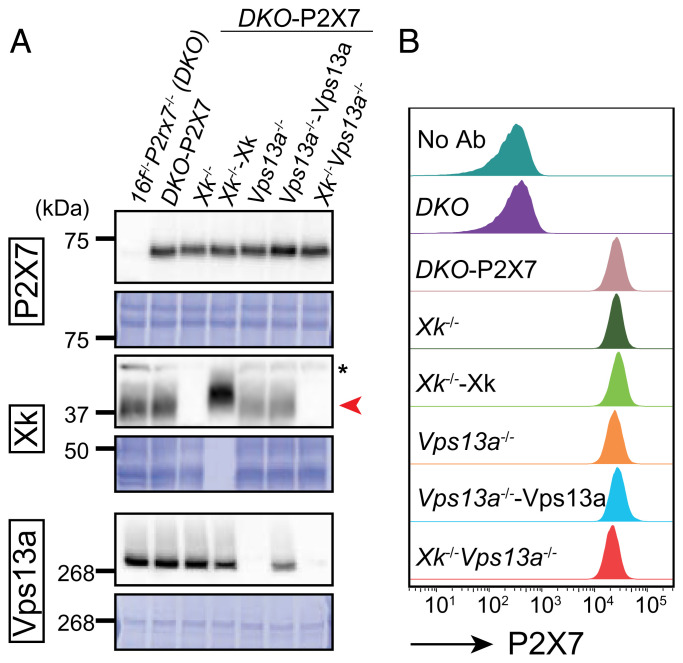
Fig. 2.
Establishment of P2X7-, Xk-, or Vps13a-deficient cell lines. (A) Western blot analysis. The P2rx7 gene in Tmem16f−/− WR19L cells was knocked out to generate 16f−/−P2rx7−/− cells (DKO). DKO was transformed with mouse P2X7 to establish DKO-P2X7. The Xk gene in DKO-P2X7 was knocked out in Xk−/−, and Xk−/−DKO-P2X7 was transformed with FLAG-tagged mouse Xk to generate Xk−/−DKO–P2X7–Xk (Xk−/−-Xk). In Vps13a−/−, the Vps13a gene was knocked out in DKO-P2X7, and Vps13a−/−DKO-P2X7 was transformed with mouse Vps13a in Vps13a−/−–Vps13a. In Xk−/−Vps13a−/−, Xk, and Vps13a genes were knocked out in DKO-P2X7. Approximately 4.7 μg of protein per lane (except for Xk−/−–Xk containing 94 ng of protein) of whole-cell lysates was separated by SDS-PAGE. Western blotting was performed with Abs against P2X7, Xk, and Vps13a, and membranes were stained with CBB. The red arrowhead shows Xk. *, non-specific band. (B) The cell-surface expression of P2X7. DKO, DKO-P2X7, Xk−/−, Xk−/−–Xk, Vps13a−/−, Vps13a−/−–Vps13a, and Xk−/−Vps13a−/− cells were stained with Alexa 647–anti-P2X7 Ab. The Alexa 647-staining profiles in the SYTOX Blue-negative population are shown.