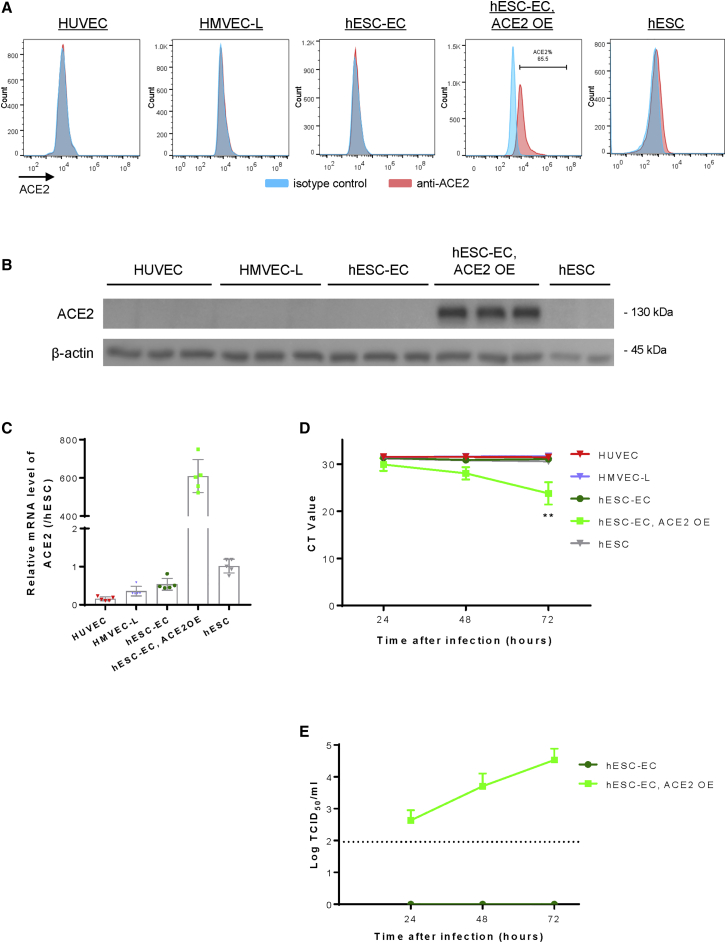
Figure 2.
ACE2 expression is required for SARS-CoV-2 infection in human ECs
(A) Flow cytometry, (B) western blotting, and (C) qRT-PCR analyses respectively, showing a lack of cell surface and cellular expression of ACE2 in HUVEC, HMVEC-L, hESC-ECs, or hESCs compared with that of hESC-ECs after lentiviral vector-mediated ACE2 expression (ACE2 OE). (D) qRT-PCR analysis showing the lack of nucleocapsid (N) gene expression at 24, 48, and 72 h after inoculation with SARS-CoV-2 in ACE2-deficient HUVEC, HMVEC-L, hESC-ECs, or hESCs compared with that of hESC-ECs with ACE2 OE. (E) Median tissue culture infectious dose (TCID50) analysis showing a time-dependent increase in the infectivity of SARS-CoV-2 in ACE2-expressing but not -deficient hESC-ECs. (C–E) Data are presented as mean ± SD, n = 5 in (C) and n = 3 in (D and E), differences were determined by one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s HSD post hoc test, ∗∗p < 0.01.