Figure 2. Acute hepatic GABA-transaminase knockdown improves obesity-induced metabolic dysfunction.
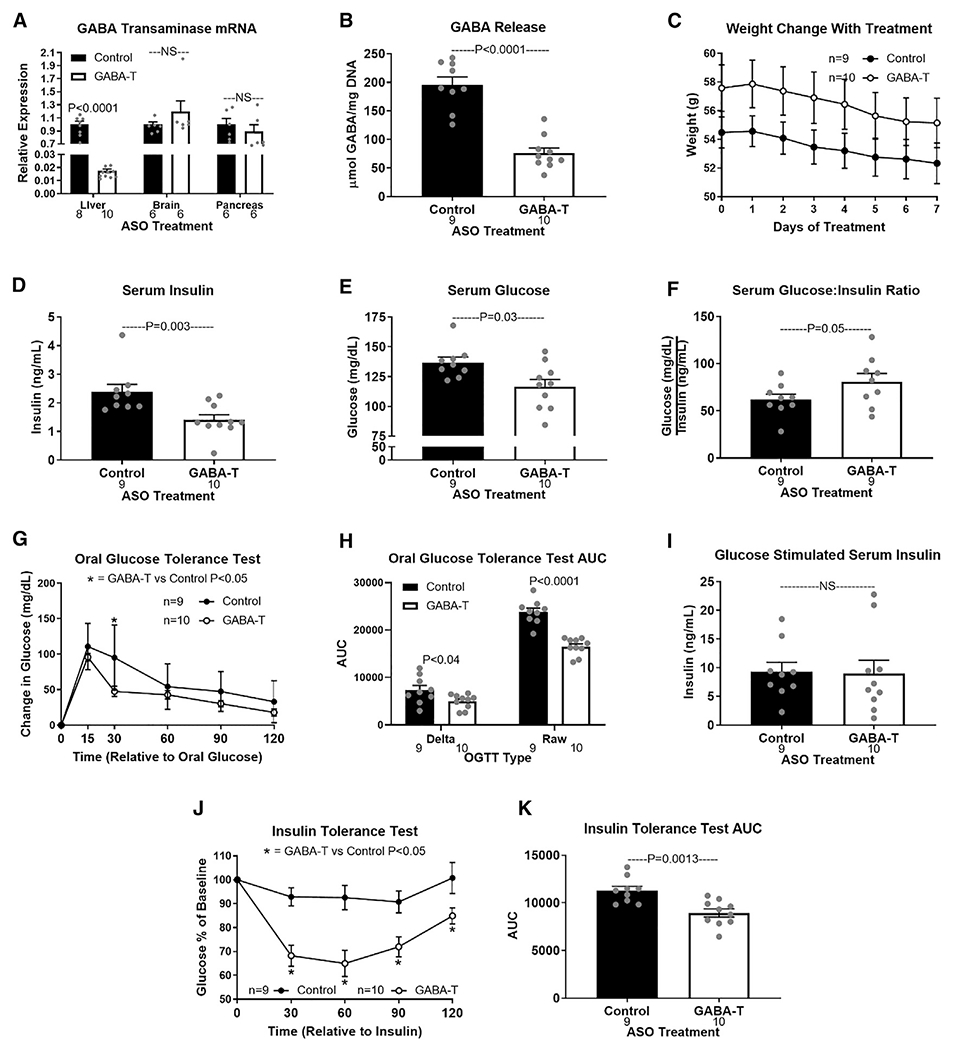
(A) GABA-T mRNA expression in liver, whole brain, and pancreas after 1 week of injections with a GABA-T targeted or scramble control antisense oligonucleotide (ASO) (12.5 mg/kg i.p. twice weekly) in high-fat-diet-induced obese mice.
(B) Release of GABA (μmol/mg DNA) from hepatic slices.
(C) Body weight during treatment.
(D–F) Basal serum insulin (D), glucose (E), and glucose:insulin ratio (F).
(G–K) OGTT (G), OGTT AUC (H), oral glucose-stimulated serum insulin (I), ITT (J), and ITT AUC (K).
Number below bar denotes n per group. All data are presented as mean ± SEM.
