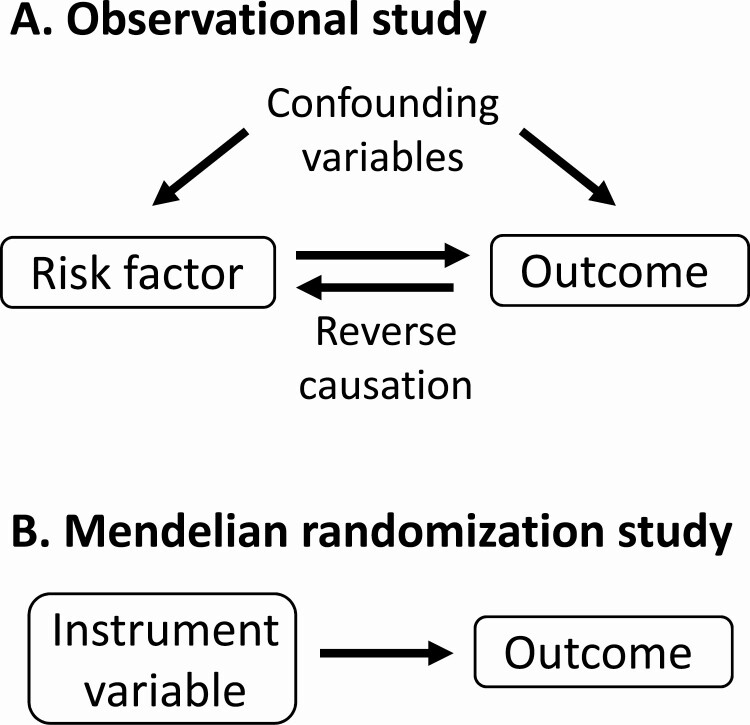
Figure 1.
Advantage of Mendelian randomization over observational studies. (A) Observational studies can demonstrate association between a risk factor and a possible outcome but provide limited information on causation because the relationship may be mediated by confounding variables or reverse causation. (B) In Mendelian randomization, the risk factor is replaced by a genetic instrument variable that strongly represents the risk factor, avoiding the effect of confounding variables or reverse causation. This allows a more robust analysis of possible causation.