Extended Data Fig. 5. Comparison of genera and functional annotations from genes and proteins correlated to disease severity in CD subtypes.
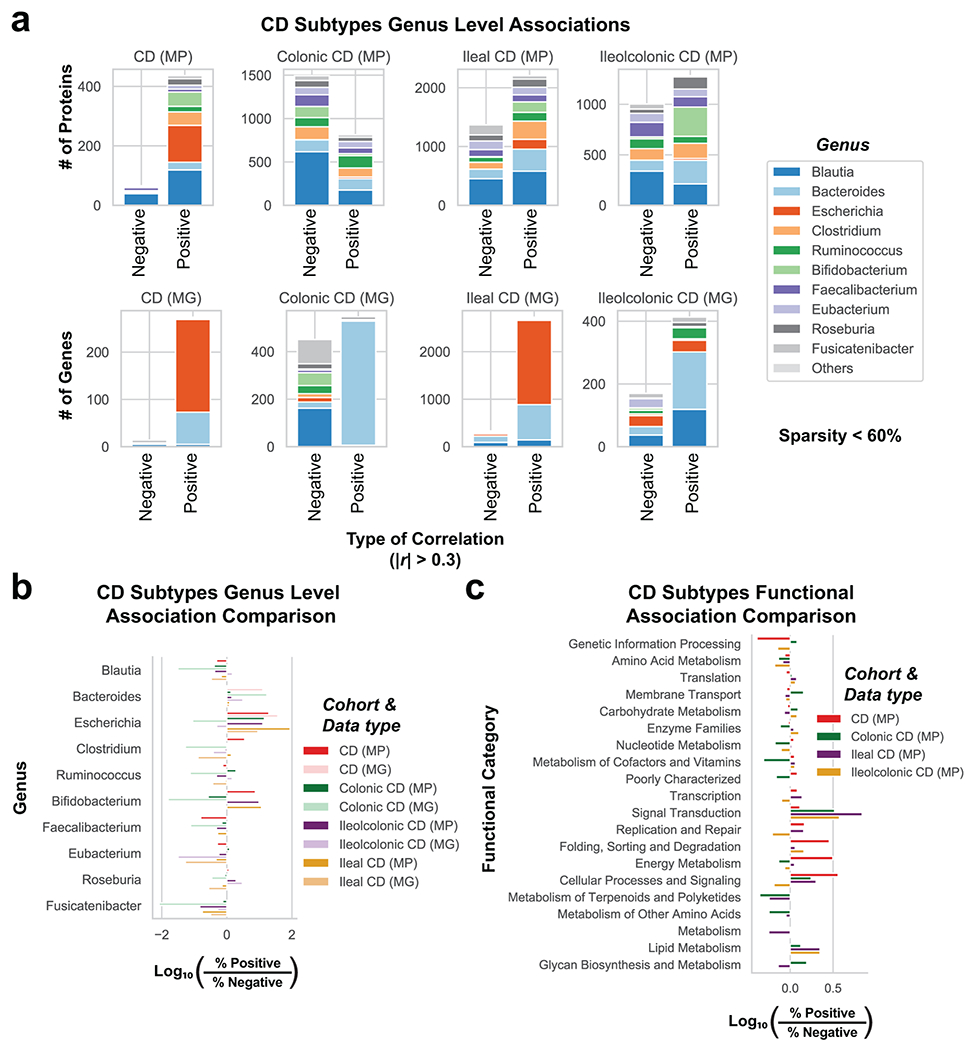
a, Genus level barcharts of significantly correlated genes or proteins stratified by CD subtype. The genus composition of genes and proteins from either the MG or MP were correlated to CDAI and shown in stacked bar charts. Only genes or proteins with |r| > 0.3 from linear regression were included, and the top 10 genera are displayed with other genera compiled into an “Others” category. b, CD subtypes genus level association comparison. The portion of genes or proteins correlated with disease activity from (a) are plotted by a Log10 comparison between the proportion of positive to negative correlations. Genes correlated to disease activity from the MG when filtering out genes appearing in less than 40% of patients within each category. c, CD subtypes functional association comparison. This analysis is analogous to (b) but summarizing the associations to KEGG functional category annotations in the MP.
