Extended Data Fig. 2. A multiplexing approach improves the depth and sparsity of metaproteomics data.
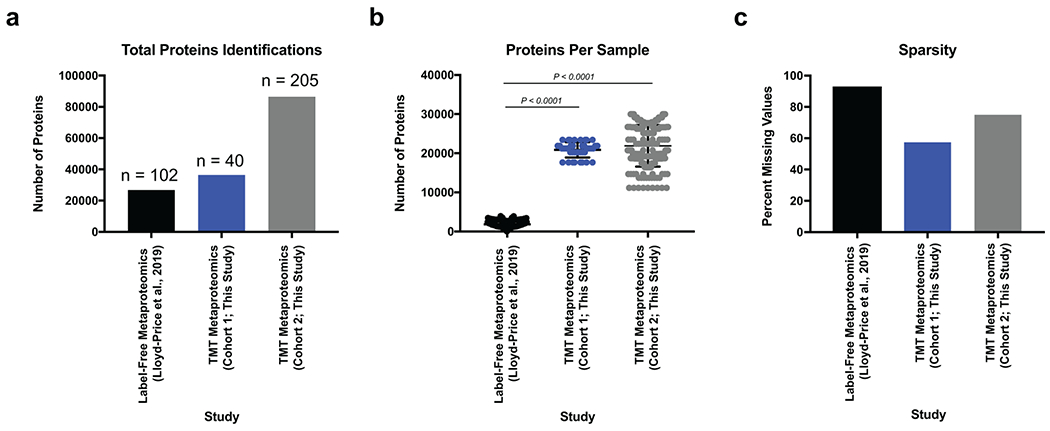
a, Multiplexed metaproteomic methods increase the total number of proteins quantified. Shown is a bar graph showing the total number of proteins identified when using identical database methodology between the 102 UC samples from the IBD multiomics database, the 40 UC samples from cohort 1 of this study, and the 205 samples from cohort 2 of this study. b, Multiplexed metaproteomic methods improve the number of proteins quantified per sample. Displayed are the mean +/− SD of the proteins identified per sample from studies shown in (a). Data derived from n=102, 40, 205 biologically independent samples as described for (a). One-way ANOVA p-values adjusted for multiple comparisons are shown (P < 0.0001). c, Multiplexed metaproteomic methods decrease the sparsity of metaproteomic studies. The percentage of missing quantification values for proteins in each data set is shown.
