Figure 5. Influence of immunoglobulin A (IgA) on gut microbiota in hypertension.
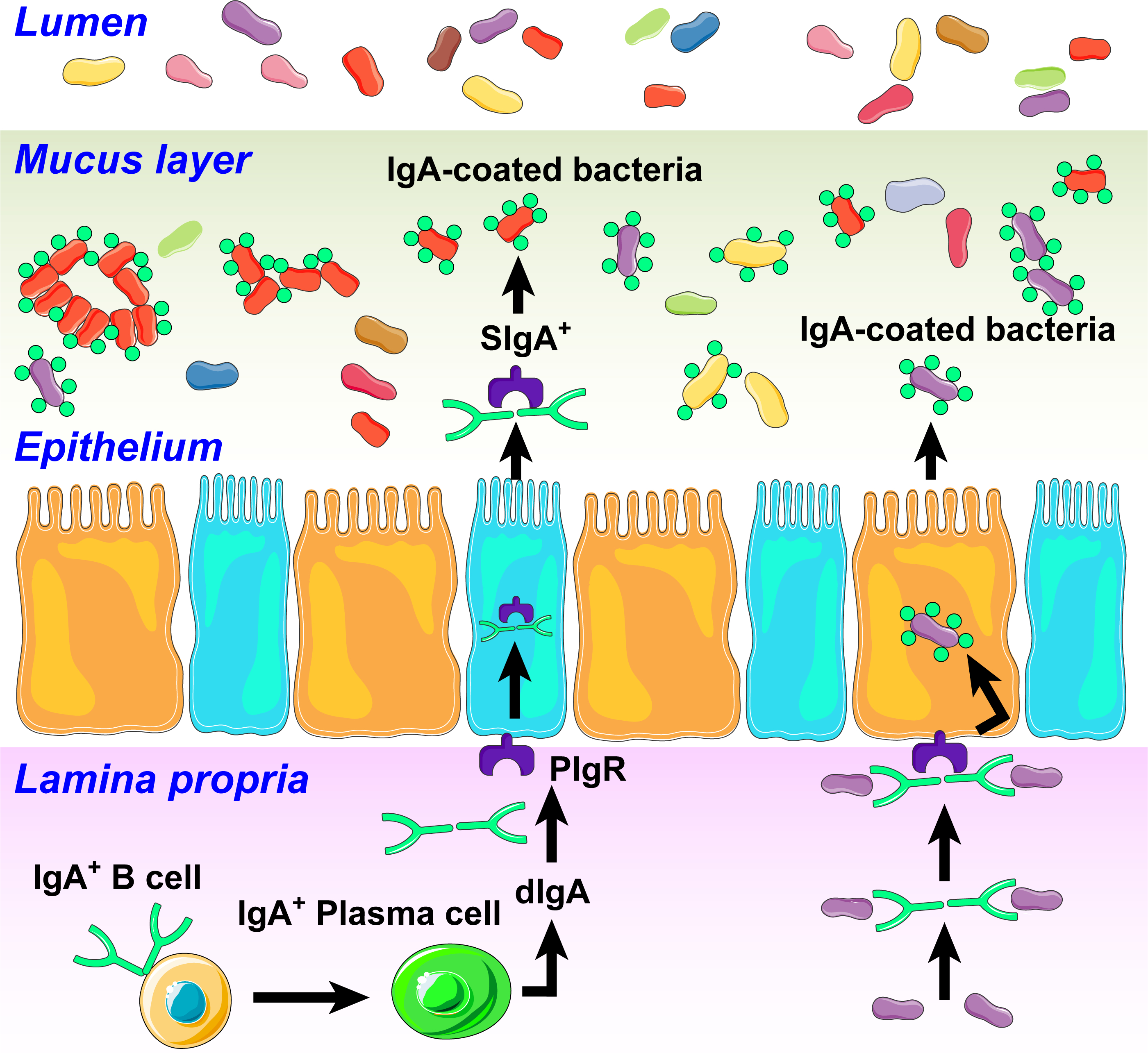
In response to antigenic signals, in part generated by an altered microbiota, IgA B cells are activated into plasma cells to produce dimeric IgA (dIgA). dIgAs bind to polymeric Ig receptors (PIgR) expressed on the basolateral side of the epithelial cells. This complex is then transported to the apical surface, where PIgR is cleaved to generate secretory IgA (SIgA). SIgA binds and coats bacteria in an antigen-specific manner altering their functions. This could include growth inhibition, clustering and elimination of beneficial bacteria and affecting the proliferation of harmful bacteria and production of toxins. We also propose that HTN-specific IgA bound bacteria taxa could translocate to the brain through leaky gut and BBB to induce neuroinflammation.
