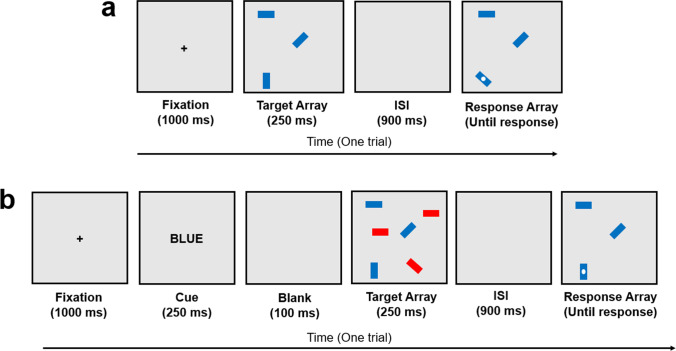
Fig. 7.
Visual arrays task. In this version of the task (see Shipstead et al., 2014), an array of rectangles briefly appears, disappears, and then reappears with one rectangle probed with a white dot. The respondent is asked to indicate whether this probed rectangle changed orientation from the initial display. Accuracy performance is typically converted into a capacity (k) score to estimate how many items the respondent can hold in primary memory. The trial shown is Set Size 3, and so 100% accuracy on a series of such trials would produce a k score of 3, whereas 50% (chance) performance would produce a k score of 0. a No distractors present (nonselective visual arrays). b Respondent is cued to attend to only a subset of the to-be-presented stimuli, and distractors are presented with the targets (selective visual arrays). Not to scale