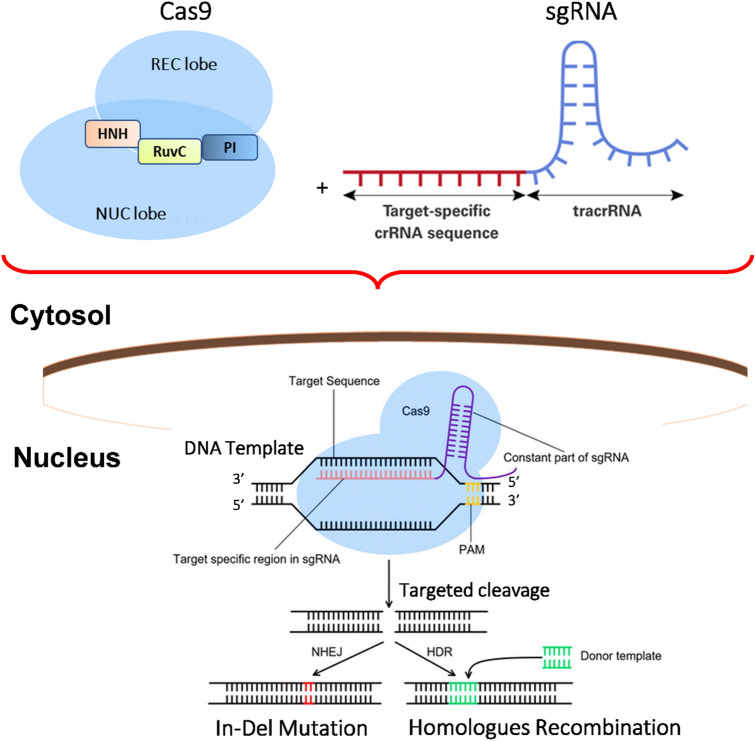
Fig. 5.
The mechanism of Cas9 cleavage of crRNA-tracrRNA target DNA. When the Cas9-crRNA-tracrRNA complex attaches to PAM-containing foreign DNA, Cas9 releases the double strands of genetic Material, allowing crRNA and foreign DNA to form a duplex. The REC lobe as well as the NUC lobe constitutes two separate components of Cas9. The REC lobe senses nucleic acid. The HNH, RuvC, and C-terminal regions of the NUC lobe are connected by a PAM (PI) interaction domain. The HNH and RuvC domains cleave the DNA strand to form a duplex of crRNA and other DNA, resulting in a double-stranded break in the target DNA