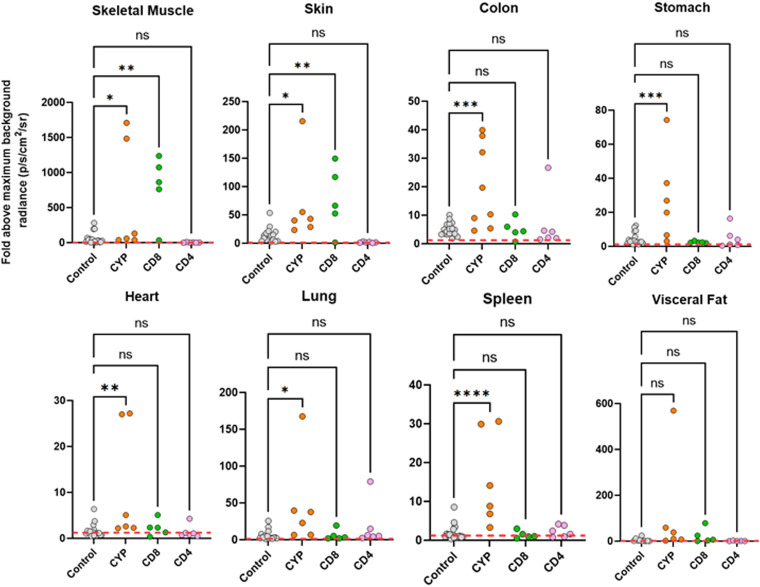
FIG 2.
Fold change in radiance (photons/s/cm2/sr) established by ex vivo bioluminescence imaging of internal tissues and organs from C3H/HeN mice chronically infected with T. cruzi (control) and after treatment with cyclophosphamide (CYP), anti-CD4, or anti-CD8 antibodies, as indicated (Materials and Methods). Infection intensities were determined using LivingImage software to draw individual regions of interest around each organ and tissue sample (17). Data from infected mice were normalized to account for variations in background radiances of different tissue types by using matching tissues from uninfected controls to establish the fold change. The maximal value from the uninfected organs was used. The dashed line indicates the detection threshold, equal to the mean +2 SD of the bioluminescence background derived from the fold change between empty regions of interest in tissue from age-matched uninfected mice and empty regions from chronically infected animals. Control data points also include values from additional immunocompetent chronically infected mice (n = 17) (18). Means were compared with a one-way ANOVA with post hoc Dunnett’s pairwise comparisons test. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001; ns, not significant.