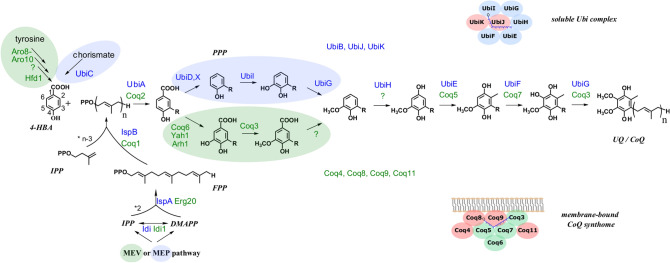
Fig. 1.
Comparative view of the eukaryotic (S. cerevisiae) and prokaryotic (E. coli) CoQ/UQ biosynthesis pathways. The proteins are in blue (E. coli) or green (S. cerevisiae), and the steps that differ between both organisms are highlighted. The numbering of the carbon atoms applied to all intermediates is given for 4-hydroxybenzoic acid (4-HBA) and the polyprenyl chain (n = 6 for S. cerevisiae, n = 8 for E. coli, n = 10 for CoQ10, the CoQ form found in humans) is depicted by R on all intermediates derived from 4-HBA. The Ubi complex and the CoQ synthome illustrate the supramolecular organization of some proteins of the pathways (enzymes in green/blue, accessory proteins in pink). Isopentenyl diphosphate (IPP), dimethylallyl diphosphate (DMAPP) and farnesyl diphosphate (FPP) are building blocks for the synthesis of the polyprenyl diphosphate tail which is added onto 4-HBA by UbiA/Coq2