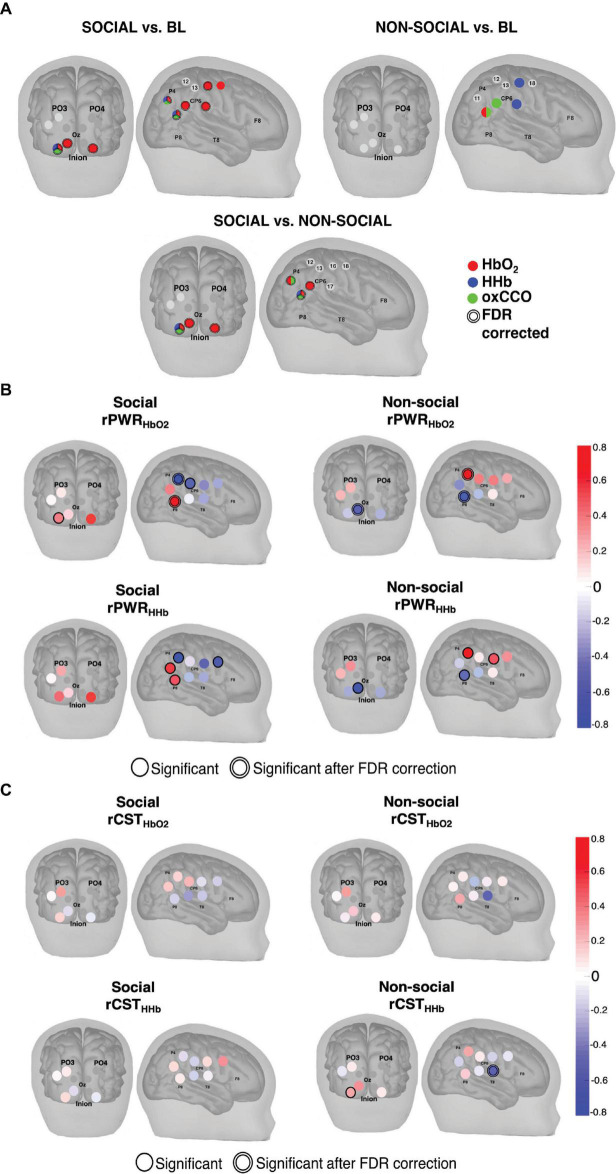
FIGURE 7.
(A) Channels with statistically significant responses for (Top, Left) the Social condition versus baseline, (Top, Right) the Non-social condition versus baseline and (Bottom) the Social versus the Non-social condition for HbO2 (red), HHb (blue) and ΔoxCCO (green). The double line around the channel indicates statistical significance after FDR correction. (B) Activation maps resulting from the group-level one sample t-test against 0 performed on the Social condition rPWR values (Top, Left) for HbO2 and (Bottom, Left) for HHb and the Non-Social condition rPWR values (Top, Right) for HbO2 and (Bottom, Right) for HHb. (C) Activation maps resulting from the group-level one sample t-test against 0 performed on the Social condition rCST values (Top, Left) for HbO2 and (Bottom, Left) for HHb and the Non-Social condition rCST values (Top, Right) for HbO2 and (Bottom, Right) for HHb. Shaded circles represent the rPWR or rCST value and a single black line represents significance (p < 0.05) while a double black line indicates significance after FDR correction A positive rPWR value implies a positive association between oxCCO and HbO2/HHb. This means that relative to the other channels, channels with a positive rPWR have a greater concurrent increase in HbO2 and oxCCO and a decrease in HHb and an increase oxCCO. A negative rPWR value corresponds to a negative association between oxCCO and HbO2/HHb. This means that relative to other channels, channels with a negative rPWR have a greater concurrent decrease in HbO2 and oxCCO and a greater increase in HHb and decrease in oxCCO. Relative to the other channels, channels with a positive rCST are those where metabolic activity exceeds haemodynamic activity. Channels with a negative rCST are those where haemodynamic activity exceeded metabolic activity.