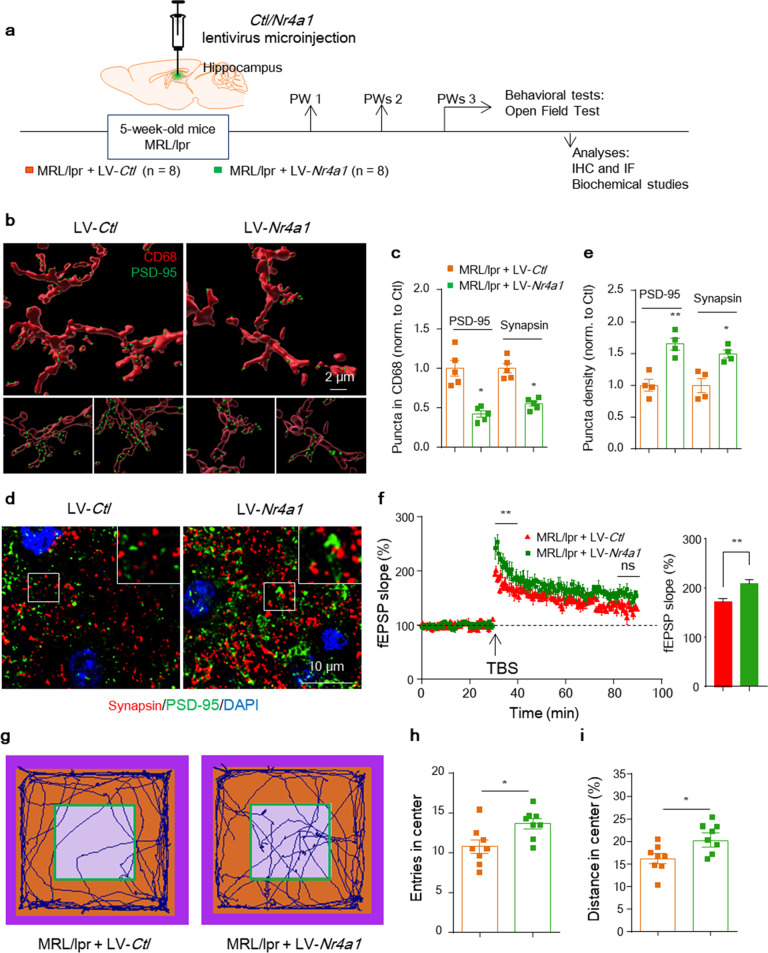
Fig. 7.
Rescuing neuronal Nr4a1 in lupus mice protects synaptic elimination, restores hippocampal microcircuit function, and mitigates anxiety-like behaviors. a Timeline of the experimental procedure in the lupus-prone mouse model. b and c Representative confocal stacks of CD68+ lysosomes (red) and engulfed PSD-95 (green) puncta in the CA1 region of MRL/lpr mice injected with the control or Nr4a1 lentivirus. Scale bar, 2 μm. (c) Quantitation of engulfed PSD-95 and synapsin puncta in CD68+ lysosomes normalized to LV-Ctl-injected mice, with 22-25 cells/group and 5 mice per group. d and e Synapsin (red) and PSD-95 (green) puncta in STED images from the CA1 region of MRL/lpr mice injected with the control or Nr4a1 lentivirus. Scale bar, 10 μm. e Quantitation of the relative number of PSD-95 and synapsin clusters normalized to LV-Ctl-injected mice, with 12 slices/group and 4 mice per group. f Long-term potentiation (LTP) was induced by theta-burst stimulation over 60 min to evaluate synaptic plasticity in LV-Ctl- and LV-Nr4a1-injected MRL/lpr mice. The LTP magnitude averaged from the first and last 10 min of recordings represents the induction and maintenance of LTP, with the average from the first 10 min shown in the right histogram (n = 8–10 slices from three mice per group); *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 according to repeated-measures ANOVA. g–i Parameters recorded and analyzed in the OFT (h, entries into the central area and i, distance traveled in the central area) of MRL/lpr mice injected with LV-Ctl or LV-Nr4a1 (n = 8 mice per group). *P < 0.05 according to Student’s t-test in (h), (i). The data are the mean ± SEM. See also Supplementary Fig. 9