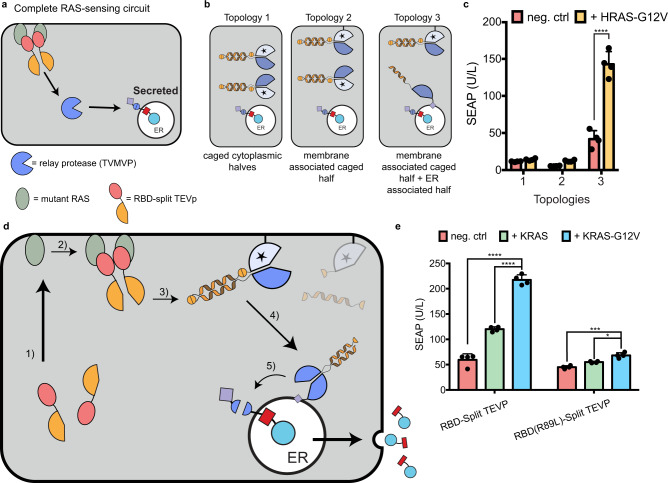
Fig. 4. RAS-sensing circuit and protease replaying pathways to activate RELEASE.
a To sense active RAS, split TEVP was fused to the RBD domain of c-RAF. RBD-split TEVP binds to active RAS at the membrane surface of the cell where the two protease halves reassociated and reconstituted protease activity. Protease activation is propagated through an intermediate protease to relay the information from the cell membrane to the ER. b Using protein localization motifs, three different topologies of intermediate protease components were created. Topology 1 uses two caged intermediate TVMVP protease halves in the cytosol. Topology 2 uses the same caged intermediate TVMVP, but with one half of the active protease localized to the membrane. Finally, Topology 3 has one half of the intermediate protease associated with the membrane, and the other half uncaged and present at the ER membrane via the p450 signal anchor sequence. The CC domain present on the uncaged TVMVP half (that was associated with the membrane) drives association with the complementary TVMVP half at the ER. c There was a significant difference in the amount of SEAP secreted when using intermediate protease topology 3, with and without mutant HRAS-G12V, compared to topologies 1, and 2. d Schematic of the signal processing of the complete KRAS-sensing circuit. The complete RAS-sensing circuit was activated by RBD-split TEVP interacting with active KRAS-G12V (1). The reconstituted TEV (2) then uncaged the membrane associated split TVMVP, releasing it from the membrane (3). The uncaged TVMVP contains a CC domain, which drives its association with the complementary CC domain present on the other split TVMVP half anchored to ER membrane (4). Finally, the reconstituted TVMVP cleaves the ER retention motif of RELEASE to secrete SEAP (5). e Using the complete RAS-sensing circuit, we observed a significant increase in SEAP secretion when expressing an active mutant variant KRAS-G12V relative to baseline levels (neg. ctrl), or wildtype KRAS. A small, but statically significant increase was also observed when using the RBD-Split TEVP containing the R89L mutation that reduced the association with active KRAS. Each dot represents an individual biological replicate. Mean values were calculated from four replicates (c, e). The error bars represent ±SEM. The results are and representative of at least two independent experiments. Significance was tested using an unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test between the two indicated conditions for each experiment. For experiments with multiple conditions, a one-way ANOVA with a Tukey’s post-hoc comparison test was used to assess significance. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001.