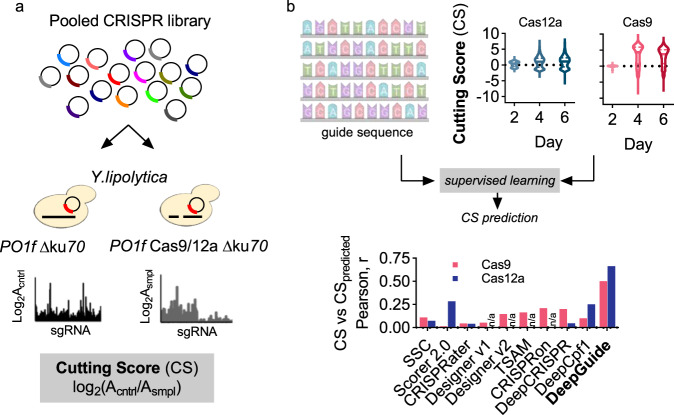
Fig. 1. Generating genome-wide CRISPR-Cas9 and CRISPR-Cas12a guide activity scores as input to machine learning algorithms for guide activity prediction.
a Pooled libraries of single-guide RNAs (sgRNAs) for Streptococcus pyogenes Cas9 and for Lachnospiraceae bacterium Cas12a were transformed into Y. lipolytica strains with non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ) DNA repair disabled by disruption of KU70. The sample strain (smpl) expresses Cas9 or Cas12a, while the control strain (cntrl) does not. The Cas12a screens were conducted for this work, while the Cas9 screens were previously reported in ref. 8. A double-stranded CRISPR cut to the genome in the absence of KU70 function leads to cell death (or a dramatic reduction in cell growth), thus enabling the quantification of guide activity through a cutting score (CS) defined as the log2 fold change of normalized guide abundance in the control vs. the sample determined by next-generation sequencing. b Genome-wide CS and sgRNA sequence are used as inputs to the convolutional autoencoder (CAE)-based learning method, DeepGuide, to predict sgRNA CS. DeepGuide prediction of Cas9 guides also used as input a normalized score for nucleosome occupancy across the genome46. The performance of established CRISPR guide prediction algorithms, including Spacer Scoring for CRISPR (SSC)29, sgRNA Scorer 2.0 (Scorer 2.0)30, CRISPRater28, Designer v1 and v227, 31, TSAM32, CRISPRon33, DeepCRISPR24, and Seq-deepCpf125, are shown as a comparison to DeepGuide. The graph shows the Pearson correlation coefficient between CS and the predicted CS for each method. DeepGuide was trained on Cas9 and Cas12a genome-wide CS, the corresponding sgRNA sequence, and genomic context, while all other algorithms used sgRNA sequence (and when appropriate, genomic context) as inputs.