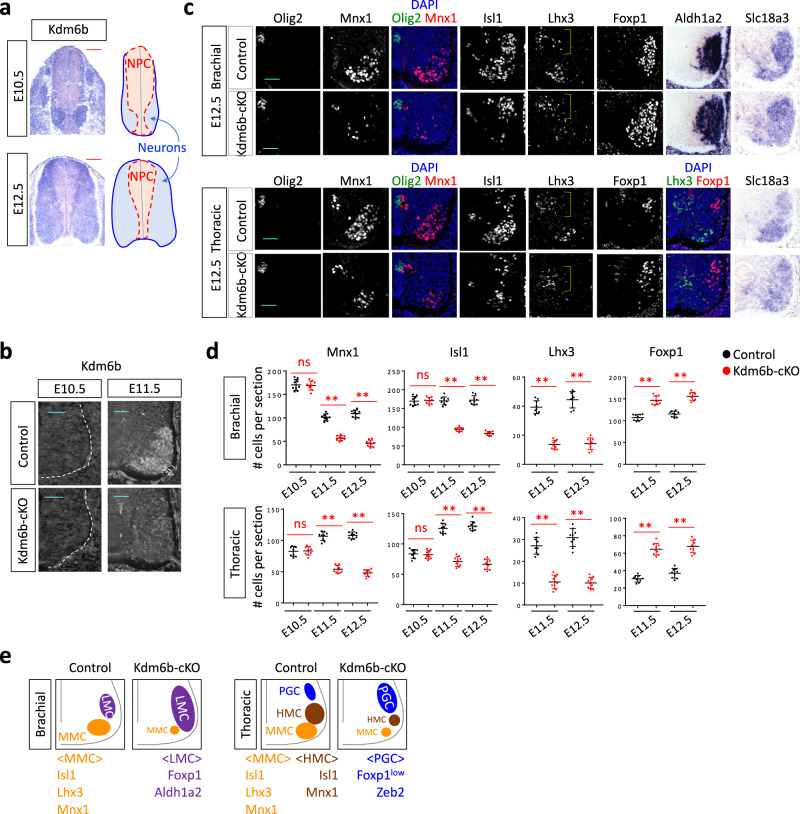
Fig. 1. Kdm6b is required for the balanced production of MN columnar subtypes.
a The expression pattern of Kdm6b in the developing spinal cord at E10.5 and E12.5, as detected by in situ hybridization analyses. Scale bars, 100 μm. The schematics depict the location of neural progenitor cells (NPC) in the ventricular zone and neurons in the mantle zone. b Immunohistochemical analysis with Kdm6b antibody shows that Kdm6b protein was detected in E11.5 control and eliminated in E11.5 Kdm6b-cKO mice. Scale bars, 50 μm. n = 3 mice per genotype. c Immunohistochemical analyses with Olig2, Mnx1, Isl1, Lhx3, and Foxp1 antibodies and in situ hybridization analyses for Aldh1a2 and Slc18a3 in the brachial or thoracic levels of E12.5 spinal cords. In E12.5 Kdm6b-cKO mice, the MNs expressing Mnx1, Isl1, or Lhx3 decreased, whereas the MNs expressing Foxp1 or Aldh1a1 increased. The brackets indicate Lhx3+ V2 interneurons. Scale bars, 50 μm. n = 3–6 mice per genotype. d Quantification of the number of MNs expressing Mnx1, Isl1, Lhx3, or Foxp1 per 12 μm thick section of the spinal cord at E10.5, E11.5, and E12.5. Mnx1+, Isl1+, and Lhx3+ MNs markedly decreased in Kdm6b-deficient mice at E11.5 and E12.5, but not at E10.5. In contrast, Foxp1+ MNs significantly increased in Kdm6b-cKO spinal cords at E11.5 and E12.5. The error bars represent the standard deviation of the mean. **p < 0.001; ns non-significant in the two-tailed Student’s t-test. n = 3–6 mice per genotype and 9 slices per genotype. Source data are provided as a Source Data file. The exact p-values are as follows. Brachial, Mnx1, E10.5, 0.83; E11.5, 7.14 × 10−11; E12.5, 3.67 × 10−12, Isl1, E10.5, 0.81; E11.5, 2.27 × 10−12; E12.5, 6.48 × 10−13, Lhx3: E11.5, 1.38 × 10−10; E12.5, 5.78 × 10−10; E11.5, 4.39 × 10−8; E12.5, 9.94 × 10−9. Thoracic, Mnx1, E10.5, 0.82; E11.5, 1.07 × 10−11; E12.5→7.33 × 10−14, Isl1, E10.5, 0.70; E11.5, 1.93 × 10−10; E12.5, 1.09 × 10−11, Lhx3, E11.5, 5.52 × 10−10; E12.5, 8.05 × 10−10, Foxp1, E11.5, 5.52 × 10−10; E12.5, 2.67 × 10−8. e Schematics for altered MN columnar diversification in Kdm6b-cKO spinal cords in comparison to control spinal cords.