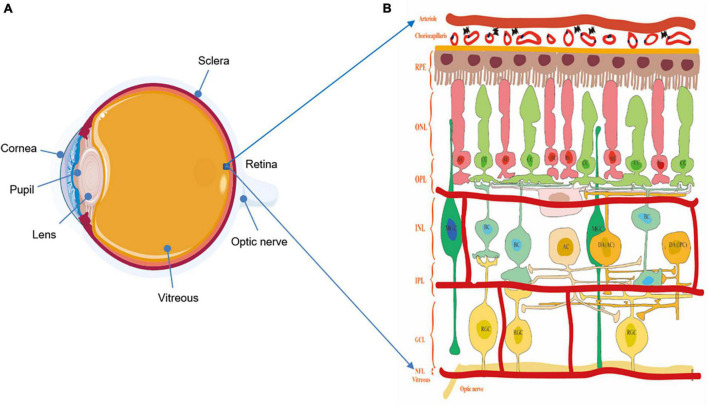
FIGURE 1.
(A) The structure of the eyeball. (B) The structure of the retina and diagram of the retinal neurons. Notably, understanding the physiologic structure and function is critical for better exploring the relationship of visual function and morphological changes. The retina possesses complex and multilayer structures and a large number of cells with microcircuits features and different functions. ILM, inner limiting membrane; RNFL, retina nerve fibers layer; GCL, ganglion cell layer; IPL, inner plexiform layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; OPL, outer plexiform layer; ONL, outer nuclear layer; ORL, outer retina layer; RPE, retinal pigmented epithelium; RC, rod cell; CC, cone cell; BC, bipolar cell; HC, horizontal cell; AC, amacrine cell; DA AC dopaminergic amacrine cell; DA IPC, dopaminergic interplexiform cell; RGC, retinal ganglion cell.