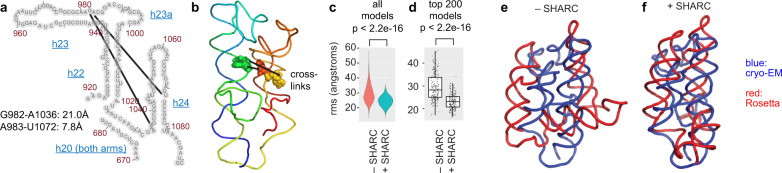
Fig. 4. Spatial distances captured by SHARC-exo improve 3D modeling.
a Secondary structure model of h22-h24, showing the two crosslinks and their distances. Only the right side of h20 is included for modeling. b 3D model of h22-h24, showing the two crosslinks (PDB: 4V6X). c, Violin plots showing the distribution of RMSD values for all models with (n = 12,363) or without (n = 20,394) SHARC-exo constraints. p values shown above were calculated with a two-sided Wilcox rank-sum test. d, Top 200 models for each condition are shown as box plots. p Value shown above the plot was calculated with a two-sided Wilcox rank-sum test. For boxplots the median is marked by the solid line in the center of the box, the verticle length of the box represents the interquartile range (IQR) upper fence: 75th percentile + 1.5*IQR, lower fence: 25th percentile − 1.5*IQR, p values for Wilcox rank-sum tests are shown above violin and boxplots. e Comparing the top model from the de novo Rosetta run (red) with the cryo-EM model (blue). f Same as panel e, except that the Rosetta model was constrained with the two SHARC-exo distances measurements. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.