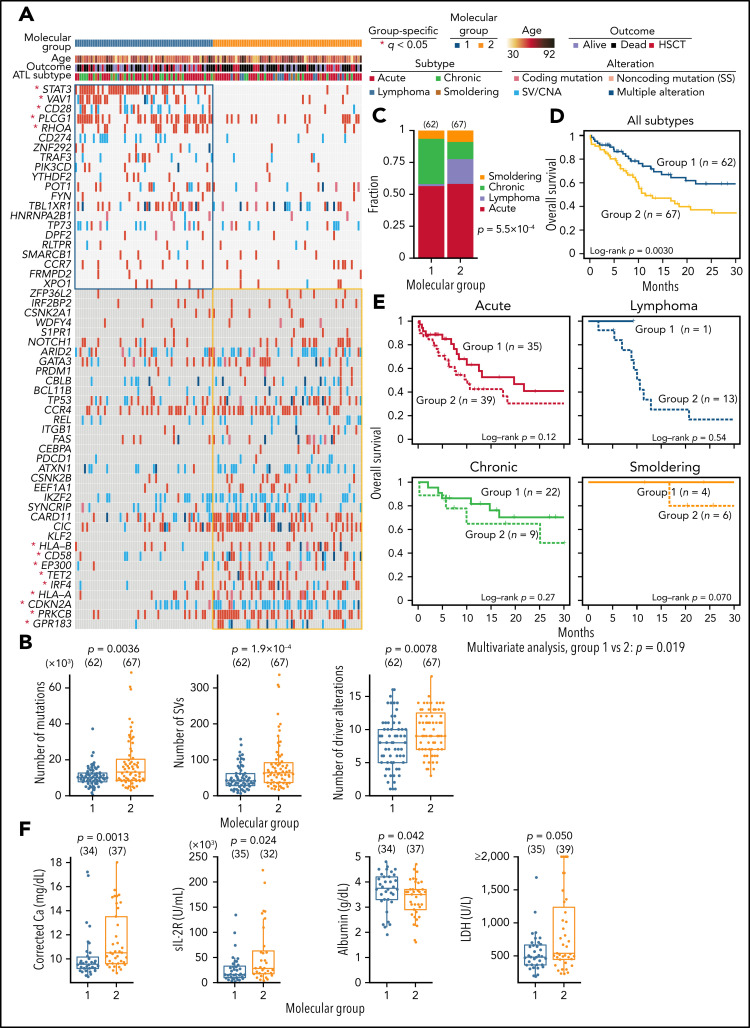
Figure 7.
Association between somatic alterations and clinical features in ATL. (A) Nonnegative matrix factorization–based consensus clustering of ATL samples using 56 driver alterations. Group 1 (n = 62) and group 2 (n = 67) cases with a silhouette score ≥0.5 are shown. *Significant group-specific genes (2-sided Fisher's exact test with Benjamini-Hochberg correction q < 0.05). (B) Comparison of number of mutations, SVs, and driver alterations between molecular groups. (C) Fraction of clinical subtypes within each molecular group. Number of cases in each group is shown in parenthesis. Two-sided Fisher's exact test. (D) Overall survival according to the molecular groups. Kaplan-Meier method with log-rank test. (E) Overall survival in each clinical subtype according to the molecular groups using Kaplan-Meier method. Log-rank test and Cox proportional hazards model (using clinical subtype as a covariate) for univariate and multivariate analysis, respectively. (F) Comparison of laboratory data in ATL cases between molecular groups 1 and 2. Two-sided Brunner-Munzel test. Calcium concentration was corrected using Payne’s formula. (A-F) Samples with silhouette score ≥0.5 were analyzed. (B,F) Two-sided Brunner-Munzel test. Box plots show medians (lines), IQRs (boxes), and ± 1.5 × IQR (whiskers). Ca, calcium; HSCT, hematopoietic stem cell transplantation; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; sIL-2R, soluble interleukin-2 receptor.