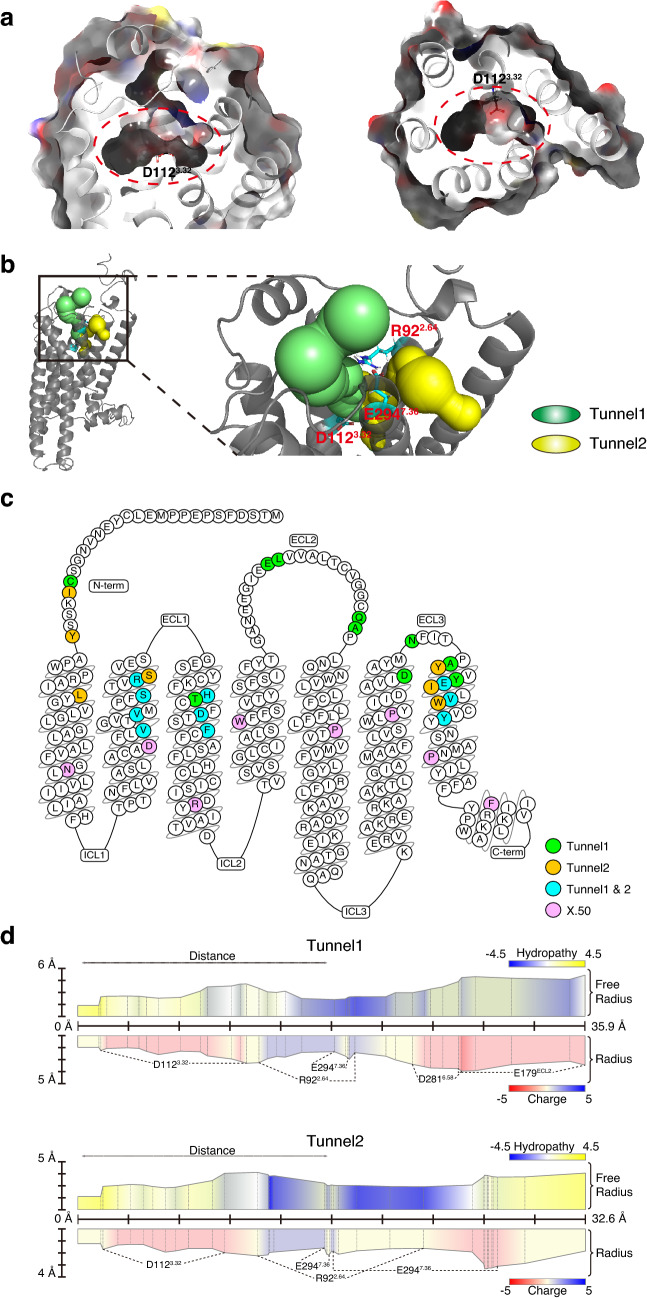
Figure 2.
Two predicted tunnels in TAAR9 are considered as pathways for ligand entry. (a) Surface (translucent, colored by residue charge) of orthosteric binding pocket (red dotted circle) in side view (left) and extracellular view (right) are located in the center of TMs. D1123.32, one of the critical binding sites, is in the center of pocket. (b) The location of Tunnel 1 (green) and Tunnel 2 (yellow) in TAAR9. Tunnel 1 and Tunnel 2, which originates from different parts of extracellular regions, converge at the known orthosteric binding site, D1123.32. The salt bridge between E2947.36 and R922.64 delineates the barrier between Tunnel 1 and Tunnel 2. (c) Snake plot for TAAR9 modified from GPCRdb (https://www.gpcrdb.org)58,59 demonstrates residues around Tunnel 1 (green), Tunnel 2 (yellow), and both tunnels (cyan). All of the residues are located at the extracellular side of the most conserved residues of each helix (pink), defined as X.50 (X represents TM) on the basis of Ballesteros–Weinstein numbering scheme13. (d) Properties (length, radius, hydropathy, and charge) of Tunnel 1 (upper) and Tunnel 2 (lower). Both tunnels are hydrophobic (yellow) in internal regions (distance from 0 Å) near the orthosteric binding site, D1123.32. Both hydropathy and charge show a distinct pattern between the middle and terminal of the tunnels. Both tunnels are hydrophilic in middle and hydrophobic or neutral in terminals. Distribution of charged residues shows negative charged residues (D1123.32, E2947.36, D2816.58, and E179 in ECL2) in two side and positive charged R922.64 in the middle of both tunnels. Distance, distance (Å) to inside terminal of tunnels. Radius, radius of sphere within tunnel limited by three closest atoms. Free Radius, radius of sphere within tunnel limited by three closest main atoms in order to allow sidechain flexibility. Hydropathy index of amino acid60, ranging from the most hydrophilic (Arg = − 4.5) to the most hydrophobic (Ile = 4.5). Charge index of amino acid is summation of the charged residues, with arginine, histidine, and lysine as + 1, and aspartic acid and glutamic acid as − 1.