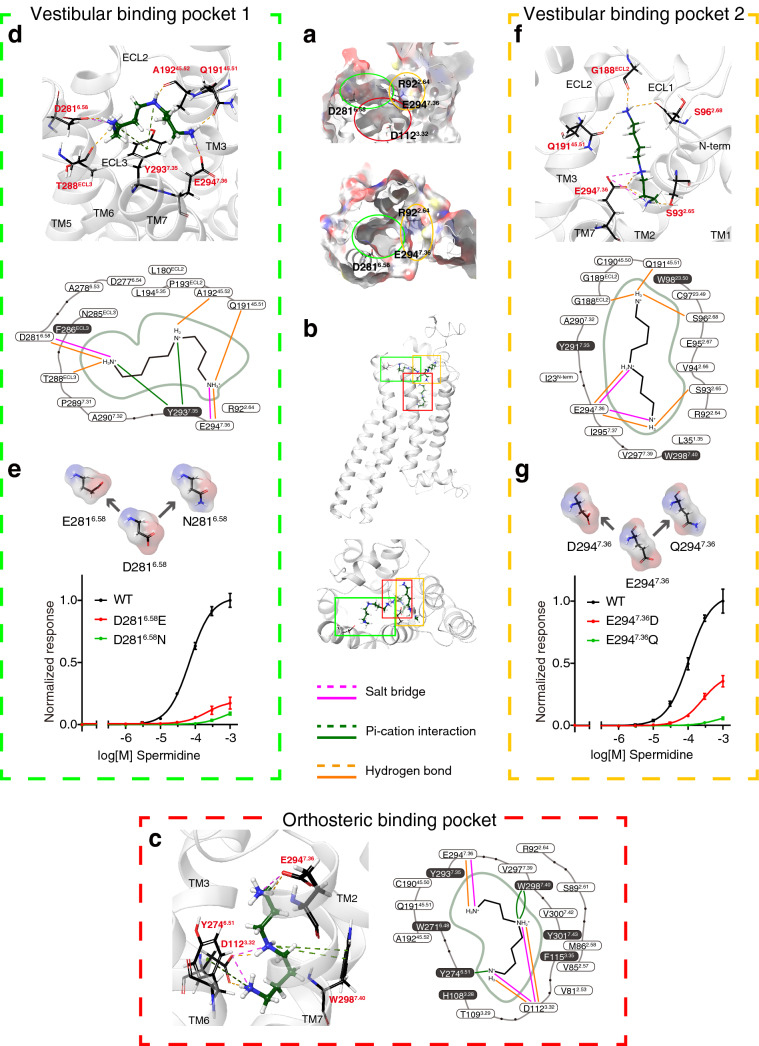
Figure 4.
Binding poses of spermidine predicted by multistep induced-fit docking. (a) Surface of vestibular binding pocket 1 centered around D2816.58, vestibular binding pocket 2 centered around E2947.36 and the orthosteric binding pocket centered around D1123.32 from side view (upper) and top view (lower). (b) Positions of spermidine docked into TAAR9 through multi-step docking. Spermidine can be docked into two vestibular binding pockets and the orthosteric binding pocket described in (a). (c) Spermidine forms non-covalent bonds with residues in the orthosteric binding pocket and is stabilized by surrounding aromatic rings. The critical binding site, D1123.32, forms salt bridges and hydrogen bonds with two amino groups of spermidine. Residues within 5 Å around spermidine were demonstrated. A relatively large proportion of amino acids have the structure of aromatic rings, forming an aromatic cage to stabilize the binding of spermidine. (d) Spermidine can be docked into vestibular binding pocket 1, forming salt bridge with D2816.58. Side chains of Q19145.51 in ECL2, Y2937.35, E2947.36, and backbones of A19245.52 in ECL2, T288 in ECL3 also interact with spermidine. 16 residues within 5 Å range of spermidine are demonstrated. Among them, only 2 have aromatic rings. (e) Key residue of vestibular binding pocket 1, D2816.58 was mutated to E with altered side chain length but preserved negative charge, and N with similar side chain length but eliminated negative charge. Dose-dependent response curves of WT, D2816.58E, and D2816.58N mutants show that mutation of D2816.58 gives rise to lower receptor responses. (f) Spermidine can be docked into vestibular binding pocket 2. Two amino groups of spermidine can interact with E2947.36 through salt bridge and hydrogen bond. In addition, side chain of S932.65 can also form hydrogen bond with spermidine. Backbones of three residues including S962.68, G188 in ECL2, and Q19145.51 in ECL2 are observed to bind to spermidine in the other terminal. Likewise, residues within 5 Å range of spermidine are demonstrated and only three of them have aromatic rings. (g) Mutation of E2947.36 to D leads to a significant decrease in receptor activity. Mutation of E2947.36 to Q almost eliminates receptor response to spermidine.