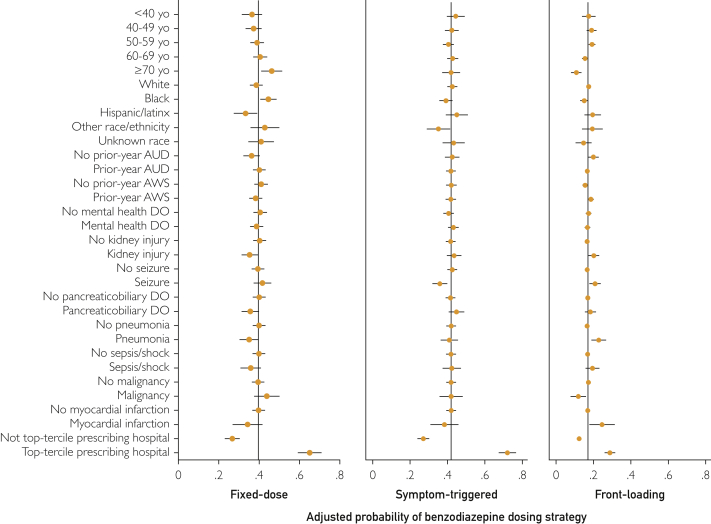
Figure 2.
Adjusted probability of fixed-dose (n=2829), symptom-triggered (n=2909), or front-loading (n=1200) benzodiazepine dosing strategies across patient characteristics and hospital prescribing pattern. Each panel shows results from a separate mixed-effects logistic regression model (one for each benzodiazepine dosing strategy) including all demographic and clinical factors, all inpatient diagnoses, and hospital as a random effect, using margins to estimate the adjusted predicted probability (Supplemental Table 5). Variables (all binary) in the model but not depicted (due to no significant association with a dosing strategy): sex (male/female), single relationship status, homelessness, nutrition/electrolyte/acid-base disorder (DO), gastrointestinal tract DO, liver injury, musculoskeletal or soft tissue DO, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, other substance use condition, cardiac dysrhythmia, diabetes mellitus, trauma, congestive heart failure. See Supplemental Table 5 for full model with results for all variables. AUD, alcohol use disorder; AWS, alcohol withdrawal syndrome; yo, years old.