Extended Data Fig. 8 |. Comparing RAD51AP1, RAD51 and RAD52 in R-loop formation.
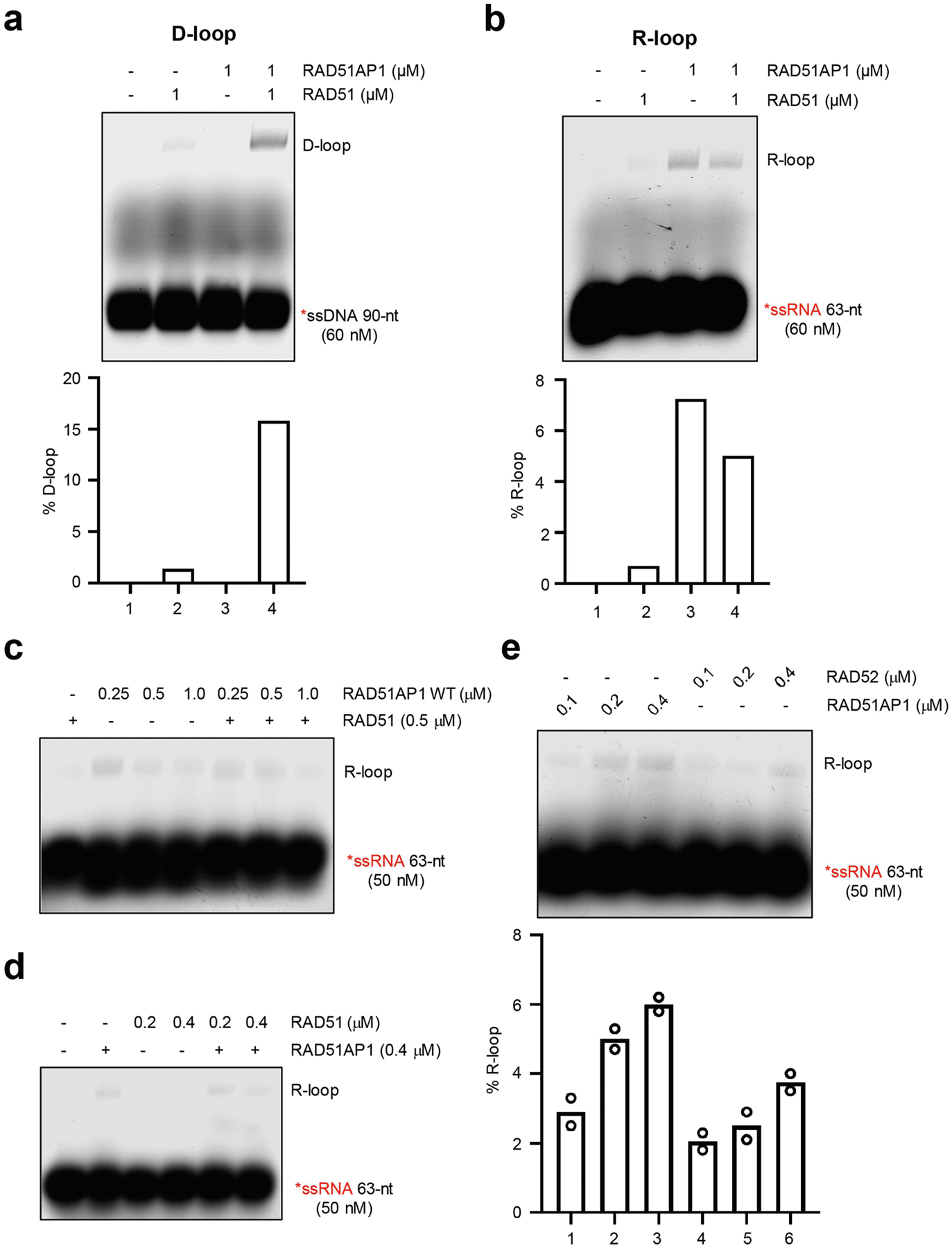
a, In vitro D-loop formation with RAD51AP1 and RAD51. RAD51 was incubated with labelled 90-nt ssDNA for 5 min and then with RAD51AP1 for another 5 min. A dsDNA plasmid containing a sequence homologous to the ssDNA was then added to the reactions. Formation of D-loops was analysed by native gel electrophoresis. The efficiency of D-loop formation was determined by quantifying the shifted and unshifted bands in a light exposure of the gel. Representative results from three similar experiments are shown. b, In vitro R-loop formation with RAD51AP1 and RAD51. RAD51 was incubated with labelled 63-nt ssRNA and then with RAD51AP1 for another 5 min. A dsDNA plasmid containing a sequence homologous to the ssRNA was then added to the reactions. The concentrations of RAD51 and RAD51AP1 are indicated. Formation of R-loops was analysed by native gel electrophoresis. Representative results from three similar experiments are shown. c, In vitro R-loop formation with RAD51AP1 and RAD51 was analysed as in b. The concentrations of RAD51 and RAD51AP1 are indicated. Representative results from three similar experiments are shown. d, RAD51AP1 was incubated with labelled 63-nt ssRNA for 5 min and then with increasing concentrations of RAD51 for another 5 min. A dsDNA plasmid containing a sequence homologous to the ssRNA was then added to the reactions. Formation of R-loops were analysed by native gel electrophoresis. Representative results from two similar experiments are shown. e, In vitro R-loop formation activities of RAD51AP1 and RAD52. Increasing concentrations of RAD51AP1 (0.1, 0.2 and 0.4 μM) or RAD52 (0.1, 0.2 and 0.4 μM) were incubated with labelled 63-nt ssRNA and then with a dsDNA plasmid containing a sequence homologous to the ssRNA. Formation of R-loops were analysed by native gel electrophoresis. The efficiency of R-loop formation was determined by quantifying the shifted and unshifted bands in a light exposure of the gel. Data are mean (n = 2 independent experiments).
