Fig. 4. SNAI2 expression timing in quail, chick, and peafowl whole embryos.
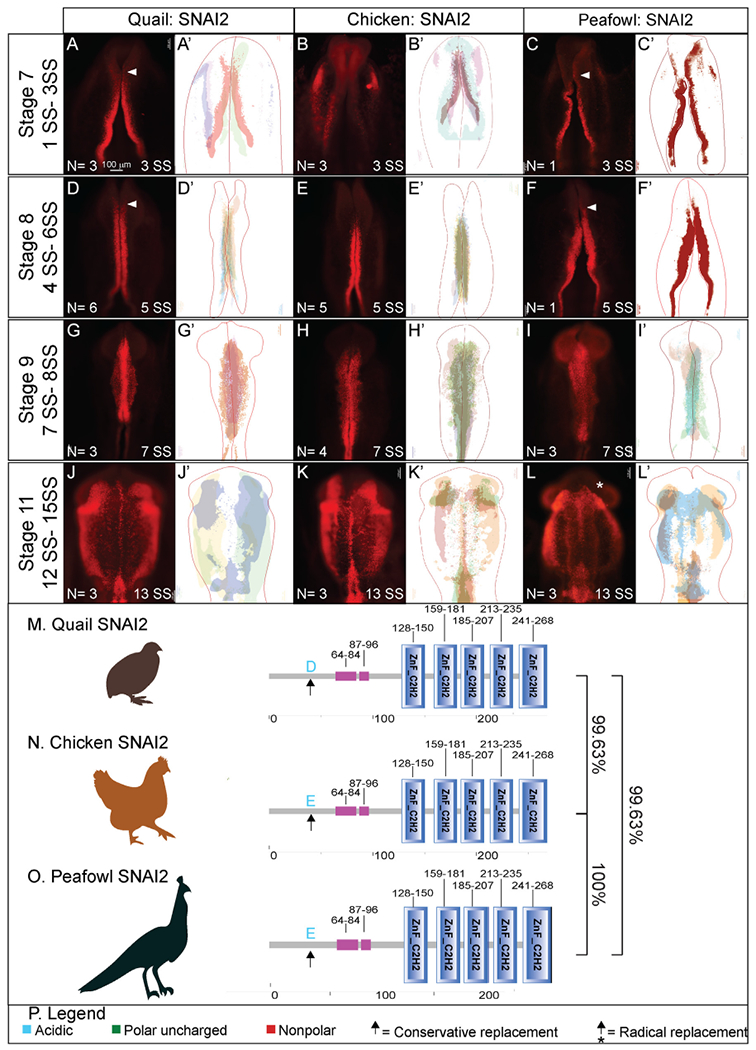
IHC for SNAI2 expression in (A-C′) HH7 (1 SS) neural plate border, (D-F′) HH8 (5 SS) dorsal neural tube, (G-I′) HH9 (7 SS) EMT stage NC cells, and (J-L′) HH11 (13 SS), neural tube and migratory NC cells. (A, D, G, J) in quail, (B, E, H, K) in chick, and (C, F, I, L) in peafowl embryos. (A′, B′, C′) schematic overlays of multiple embryos. Quail and peafowl exhibit more anterior SNAI2+ expression than chick between HH7 to HH8 (compare A, D to B, E and C, F, arrowhead). Number of embryos analyzed at each stage and used for schematic overlays indicated in IHC panels. Scale bar is 100 μm and all images were taken at the same magnification. (M–O) Amino acid sequences were aligned and compared, then analyzed in SMART to obtain domain diagrams. Zinc finger domains (blue) and small pink boxes are low complexity domains are shown on schematics. (N, O) Chick and peafowl SNAI2 proteins are identical and (M) quail SNAI2 has one conservative amino acid replacement (same type of amino acid, black arrow). (P) Legend for (M–O). Blue is acidic amino acid, green is polar uncharged, red is nonpolar. Scale bar for all whole mount images is 100 μm and is marked in the first image.
