Figure 6.
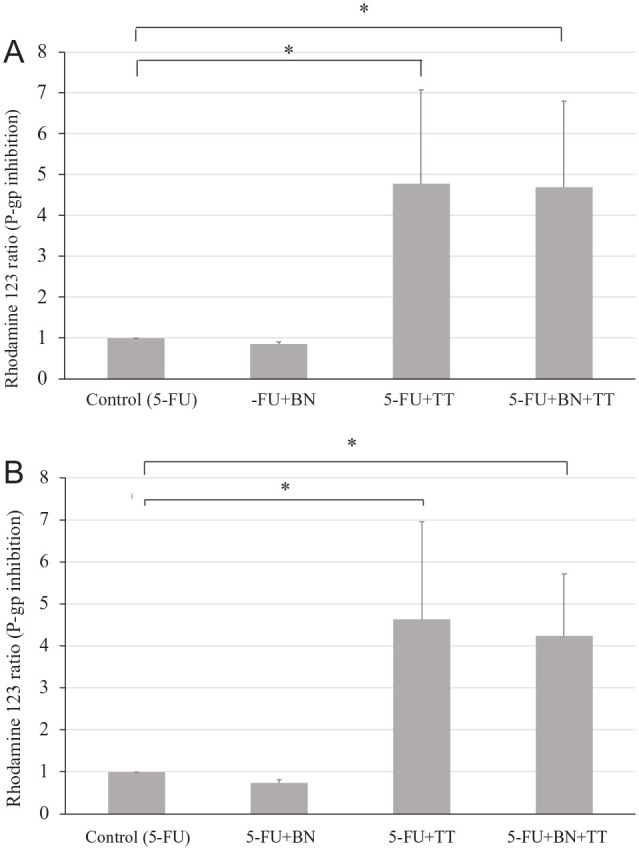
Effect of the NF-κB inhibitor on the modulatory activity of BN and TT in the BTB model. (A) Without SN50. (B) With SN50.
Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation. (A) Effect of BN and TT in the BTB model without the NF-κB inhibitor (SN50) treatment. (B) Effect of BN and TT in the BTB model following treatment with the NF-κB inhibitor SN50 (20 μM). The concentrations of the analytes borneol, tetrandrine, and 5-FU were 300, 10, and 10 μg/mL, respectively. *P < .05 (ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s test) indicates a significant difference compared to the control group (10 μg/mL 5-FU). Both the 5-FU + TT and 5-FU + BN + TT groups showed significant changes compared to the control group, which was independent of the addition of SN50. On comparing the differences between Figure 6A and B by flow cytometry, the activity of P-gp was not significantly different among the groups. According to this result, the 5-FU + TT and 5-FU + BN + TT groups could influence the function of P-gp through another pathway.
Abbreviations: 5-FU + BN, 5-FU combined with borneol; 5-FU + TT, 5-FU combined with tetrandrine; 5-FU + BN + TT, 5-FU combined with borneol and tetrandrine; BTB, blood–tumor barrier.
