Figure 9. PERK inactivation exacerbated demyelination in the PNS of adult Sel1L cKO mice.
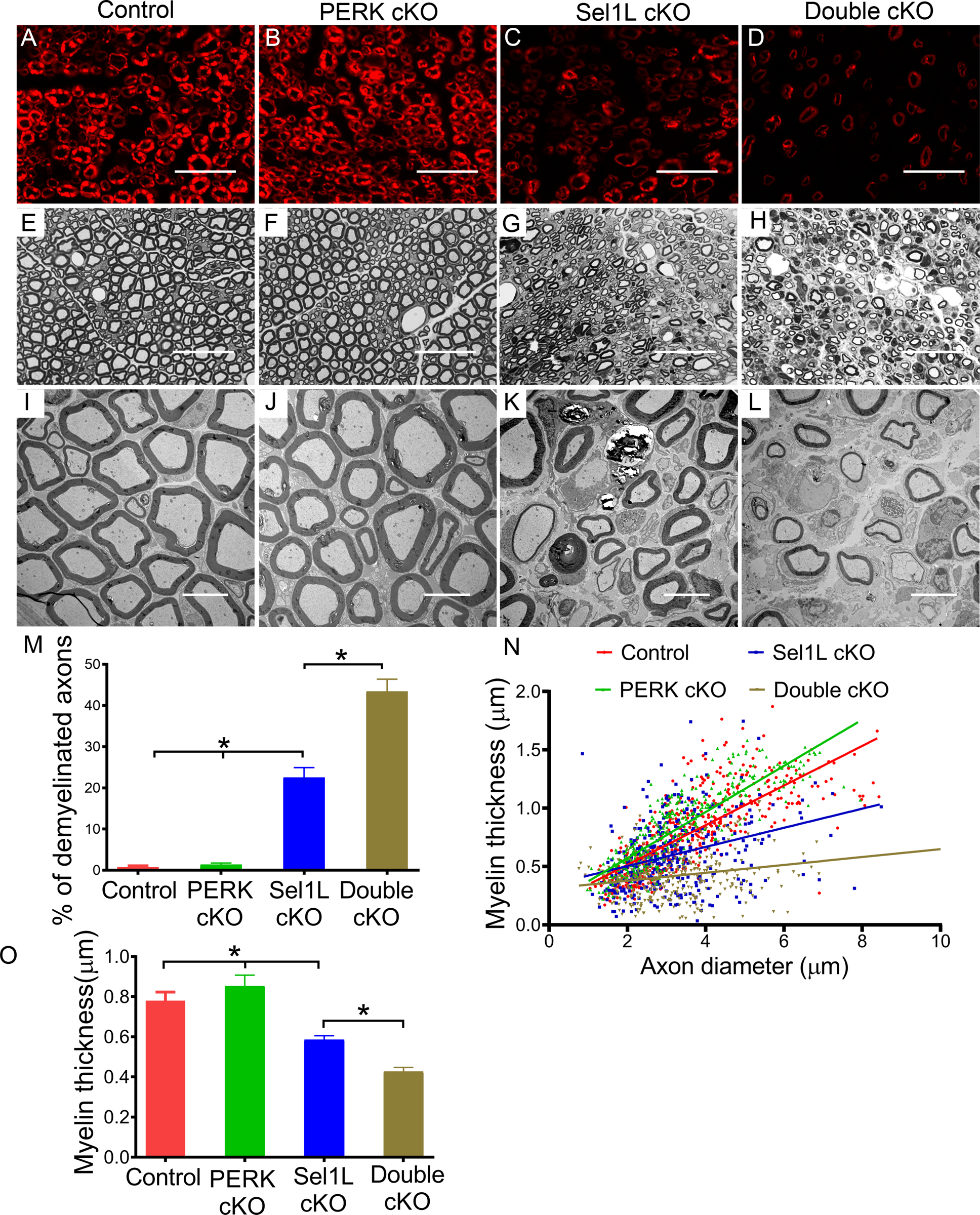
A-D. P0 immunostaining showed that P0 immunoreactivity was noticeably reduced in the sciatic nerve of 16-w-old Sel1L cKO mice compared to PERK cKO mice and control mice, and was further reduced in Double cKO mice. E-H. Toluidine blue staining showed noticeable myelin loss in the sciatic nerve of 16-w-old Sel1L cKO mice compared to PERK cKO mice and control mice, which was exacerbated in Double cKO mice. I-O. EM analysis showed that Sel1L deficiency in SCs significantly increased the number of demyelinated axons and decreased the thickness of myelin in the sciatic nerve of 16-w-old mice, which was exacerbated by PERK inactivation. Scale bars: A-H, 20 μm; I-L, 5 μm. N = 4 animals. Statistical analyses were done with a 1-way ANOVA with a Tukeys posttest. Error bars represent SD, P < 0.05.
