Fig. 2.
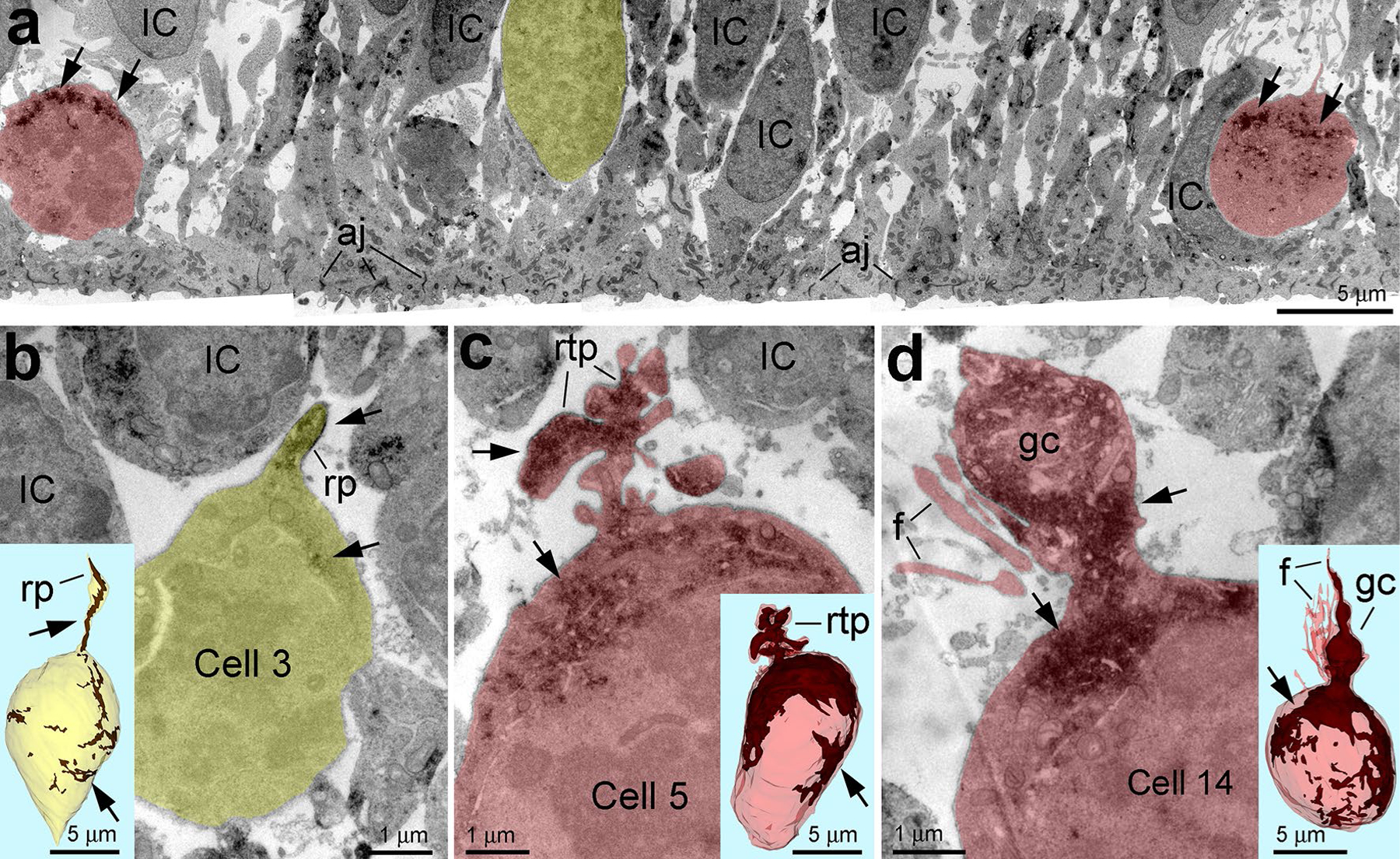
GFAP content is very variable in dividing VZ progenitors. a Differential expression of GFAP (arrows) in dividing cells in the VZ of E45 rhesus monkey embryo. Mitotic cells with low and high GFAP content are depicted semitransparent yellow and red, respectively. b–d Estimation of GFAP content in distinct cells using 3D reconstruction from uninterrupted serial sections. b Example of low GFAP expressing cell emitting potentially long radial process (rp) truncated in the serial sections. c, d High GFAP expressing cells emit short retracting-like process (rtp in c) or growth cone-like process (gc) and numerous filopodia (f in d). Insertions show 3D reconstructions of the cell bodies with GFAP immunoreaction end-product depositions (arrows; brown in the 3D images). Analyzed cells are numbered according to Table S1 and represented with basal aspect upwards. aj adherens junctions at the ventricular surface, IC interphase cells
