FIGURE 4.
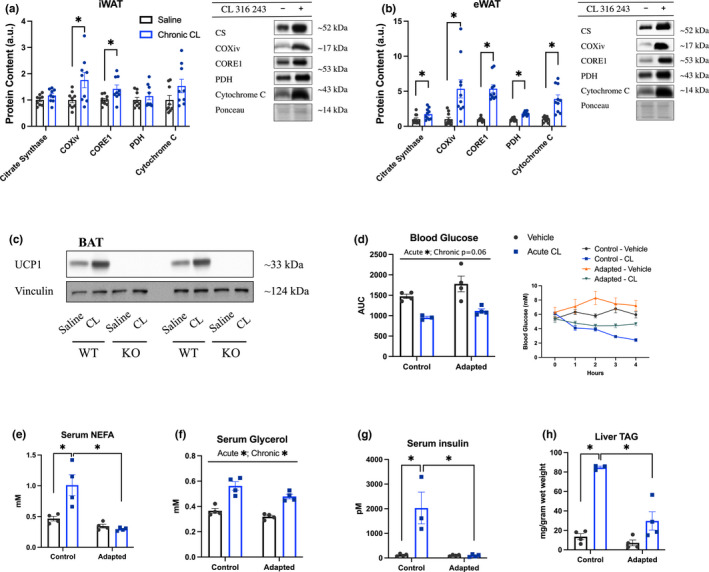
In UCP1 knockout mice the chronic effects of CL to induce mitochondrial biogenesis are intact and the acute metabolic effects of CL dissipate with repeated use. UCP1−/− mice were adapted to CL or saline injections for 6 days. On the seventh day (24 h following the last treatment) adipose depots were dissected and analyzed for protein content via western blot (a–c; n = 5–6 mice/group). Proteins of interest were expressed relative to an internal loading control from the same respective gel as the protein of interest. Please note that a ponceau stain was used for correction purposes for each protein of interest but for space purposes only one representative ponceau is shown for each tissue. UCP1 protein was undetectable in brown adipose (BAT) from treated and untreated knockout mice. In a separate cohort, mice were treated with CL or saline for 6 days then on the seventh day were treated acutely with CL or saline. Blood glucose (d; n = 3–4 mice/group) was measured each hour for 4 h for determination of AUC (glucose curve inset). Four hours following acute treatment serum, liver, and WAT depots were collected for analysis of serum NEFA (e; n = 4 mice/group), glycerol (f; n = 4 mice/group), insulin (g; n = 3–4 mice/group), and liver TAG accumulation (h; n = 3–4 mice/group). Protein content (a, b) was analyzed by two‐tailed unpaired t‐test while differences between groups in (d–h) were analyzed by two‐way ANOVA. *p < 0.05 between indicated groups. All data are presented as mean ± SEM
