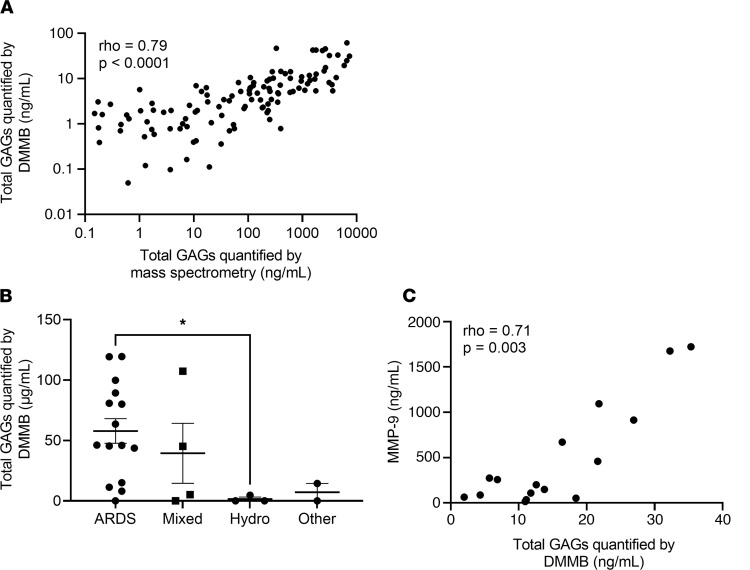
Figure 6. Point-of-care detection of alveolar epithelial glycocalyx degradation approximates mass spectrometry and is feasible in the ICU.
(A) Assessment of the relationship between GAG shedding as quantified by state-of-the-art HPLC-MS and GAG shedding as quantified by colorimetric DMMB assay. n = 132 participants in whom sufficient fluid was available to run the DMMB assay. Spearman ρ and P values are as indicated on the graph. (B) Assessment of the relationship between GAG shedding by DMMB assay and cause of respiratory failure in a second cohort of patients in whom filters were collected only at routine filter changes, rather than through a standardized research study protocol. n = 24 participants with respiratory failure. *P < 0.05 by Wilcoxon’s rank sum test. Data are presented with mean ± SEM. (C) Assessment of the relationship between GAG shedding by DMMB assay and MMP-9 expression in the cohort of patients with filters collected only as part of routine care. n = 16 participants with respiratory failure. Spearman ρ and P values are as indicated on the graph.