Figure 4. Chronic apalutamide treatment in C4-2B cells activates the steroid biosynthesis pathway through AKR1C3 upregulation.
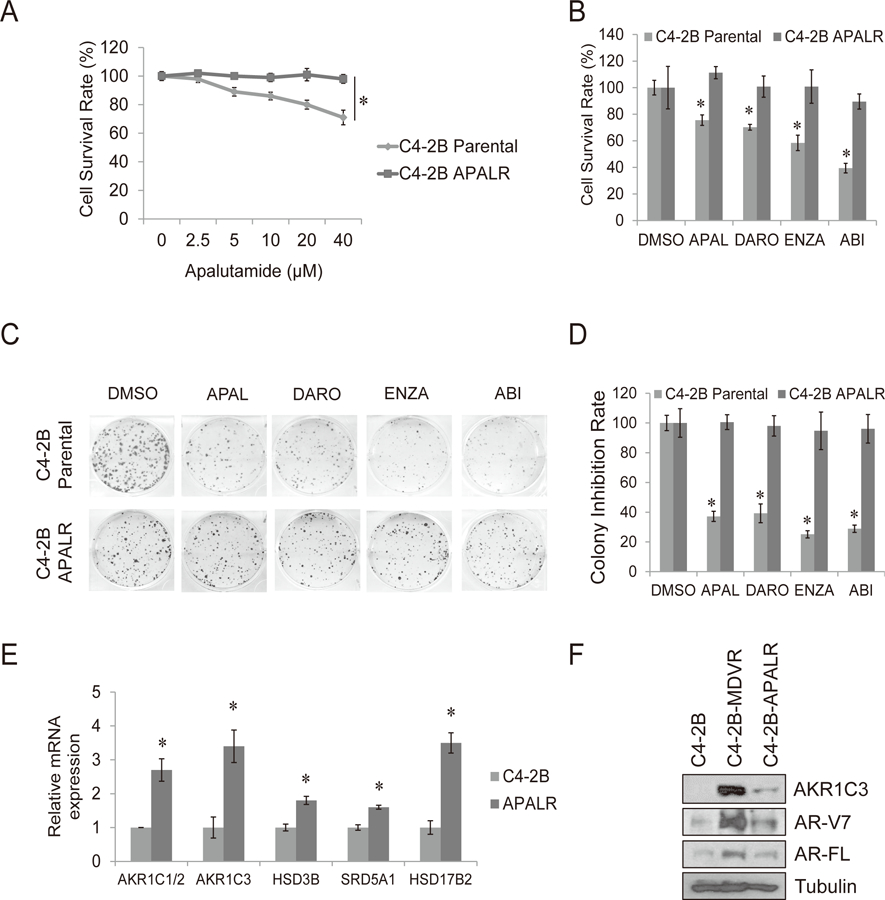
A. C4-2B parental and C4-2B APALR cells were treated with different concentration of apalutamide for 3 days, total cell numbers were determined and cell survival rate was calculated. B. C4-2B parental and C4-2B APALR cells were treated with 20 μM apalutamide, 5 μM darolutamide, 20 μM enzalutamide or 10 μM abiraterone and cell numbers were determined after 3 days. C-D. The clonogenic ability of C4-2B parental and C4-2B APALR cells treated with 20 μM apalutamide, 5 μM darolutamide, 20 μM enzalutamide or 10 μM abiraterone was analyzed. E. The genes involved in steroid hormone biosynthesis pathway were determined by qRT-PCR. F. Whole cell lysates were collected from C4-2B parental, C4-2B MDVR and C4-2B ARNR cells and subjected to western blot. Enza: enzalutamide, APAL: apalutamide, Abi: abiraterone acetate, DARO: darolutamide. * p<0.05
