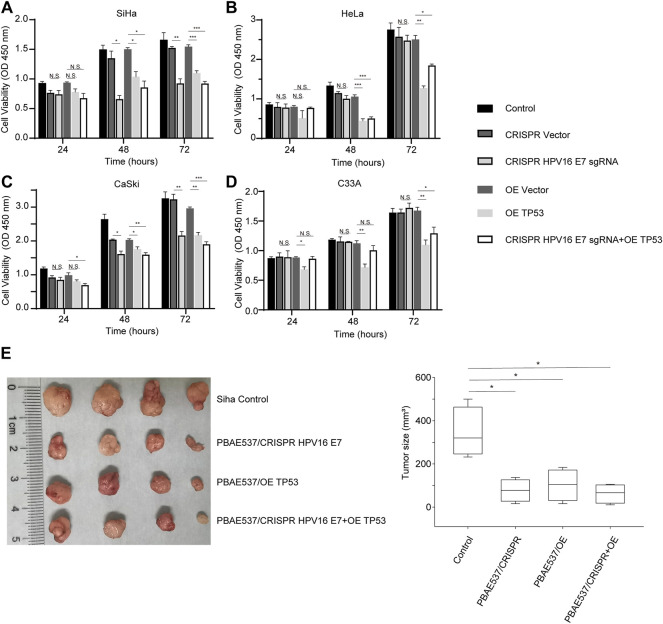
FIGURE 5.
Growth inhibition of cervical cancer cells by PBAE537–therapeutic plasmid polyplex NPs in vitro and in vivo. (A–C) The CCK-8 method was used to detect the cell viability of (A) SiHa, (B) HeLa, (C) S12, and (D) CaSki cells at 24, 48, and 72 h after treatment with nanoparticles (PBAE537/plasmid 60:1) composed of PBAE537 and three targeted plasmids (HPV16 E7 inactivation group, p53 overexpression group, and 1:1 mixture of the two plasmids group). (E, F) SiHa cells were injected subcutaneously into the right hind limb of BALB/c-nu mice. When the transplanted tumor grew to approximately 35 mm3, NPs consisting of PBAE537 and the CRISPR/Cas9 plasmid targeting HPV16 E7 and p53 were injected intratumorally (60:1). NPs were injected as a volume of 100 µL containing 60 μg of plasmid once every 4 days. (E) The subcutaneously formed tumors were photographed, and (F) the estimated sizes were measured after treatment with NPs. One-way ANOVA was used for statistical analysis, *: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.001, N.S.: no significant difference.