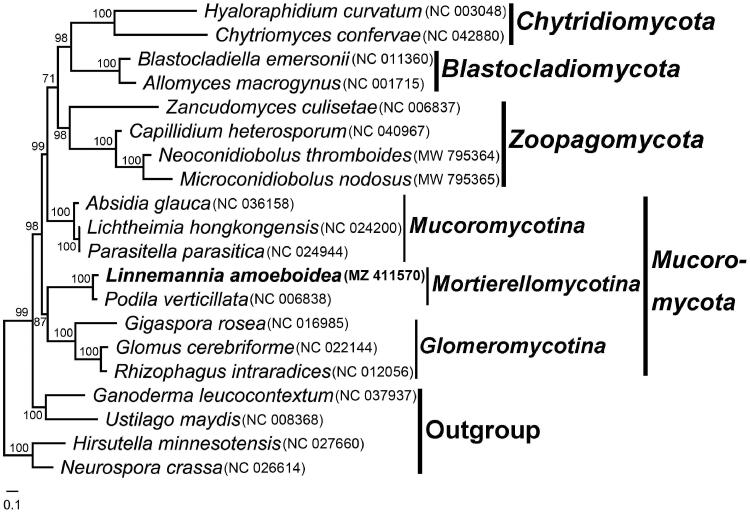
Figure 1.
The phylogenetic tree constructed based on 14 mitochondrion encoded proteins. The 14 proteins included oxidase subunits (Cox1, 2, and 3), the apocytochrome b (Cob), ATP synthase subunits (Atp6, Atp8, and Atp9), NADH dehydrogenase subunits (Nad1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and Nad4L). The following other 19 fungal mitogenomes were used in the phylogenetic analysis: Absidia glauca (Ellenberger et al. 2016), Allomyces macrogynus (Paquin and Lang 1996), Blastocladiella emersonii (Tambor et al. 2008), Capillidium heterosporum (Nie et al. 2019), Chytriomyces confervae (van de Vossenberg et al. 2018), Gigaspora rosea (Nadimi et al. 2012), Glomus cerebriforme (Beaudet et al. 2013), Hyaloraphidium curvatum (Forget et al. 2002), Lichtheimia hongkongensis (Leung et al. 2014), Microconidiobolus nodosus (Cai et al. 2021), Neoconidiobolus thromboides (Nie et al. 2021), Parasitella parasitica (Ellenberger et al. 2014), Podila verticillata (Seif et al. 2005), Rhizophagus intraradices (Lee and Young 2009), and Zancudomyces culisetae (Seif et al. 2005). Besides, Ganoderma leucocontextum (NC_037937), Hirsutella minnesotensis (Zhang et al. 2016), Neurospora crassa (NC_026614) and Ustilago maydis (NC_008368) were choosen as outgroups. Maximum likelihood bootstrap values (≥70 %) of each clade are indicated along branches. Scale bar indicates substitutions per site. The GenBank accession numbers are behind the Latin names.