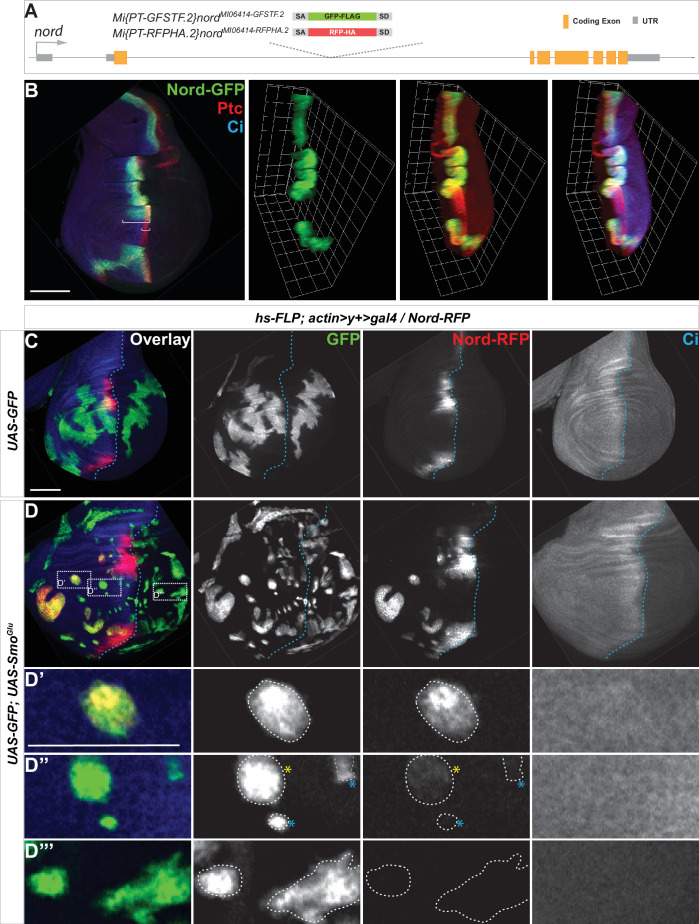
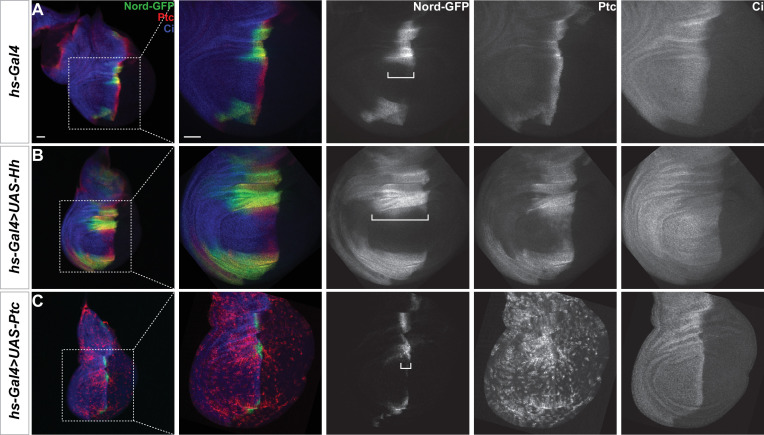
Figure 2. Hedgehog (Hh) signaling regulates nord expression in the Drosophila wing imaginal disc.
(A) Schematic diagram of the wild-type nord locus and the protein-trap alleles of nord. The EGFP-FlAsH-StrepII-3xFLAG (GFSTF) or TagRFP-T-3xHA (RFPHA) tag was inserted in the appropriate orientation and reading frame of nord, which permitted visualization of the Nord protein localization in vivo. (B) Wing imaginal discs from late third instar larvae carrying nord-GFP (Mi{PT-GFSTF.2}nordMI06414-GFSTF.2/+) were immunostained for GFP (green), Ptc (red), and Ci (blue). Maximum intensity z-projection and 3D reconstruction from a confocal image stack show nord expression in a representative wing imaginal disc. White brackets indicate the expression range of Ptc or Nord-GFP. (C, D) Wing imaginal discs from late third instar larvae carrying nord-RFP (Mi{PT-RFPHA.2}nordMI06414-RFPHA.2/+) and flip-out clones expressing the indicated UAS-transgenes were immunostained for HA (Nord-RFP, red), GFP (flip-out clones, green), and Ci (A compartment, blue). (D’–D”’) Zoomed view of the indicated area from panel (D). Note that ectopic nord-RFP is induced in UAS-SmoGlu-expressing clones located in the A compartment flanking the wing pouch (D’), but not in the P compartment (D”’). In the central wing pouch (D”), little (yellow star) or none (blue star) ectopic Nord-RFP was detected in SmoGlu-expressing flip-out clones. Dashed white lines indicate the clone boundary; dashed blue lines indicate the A/P compartment boundary, which is determined by the expression of endogenous Ci. Scale bar, 50 μm.