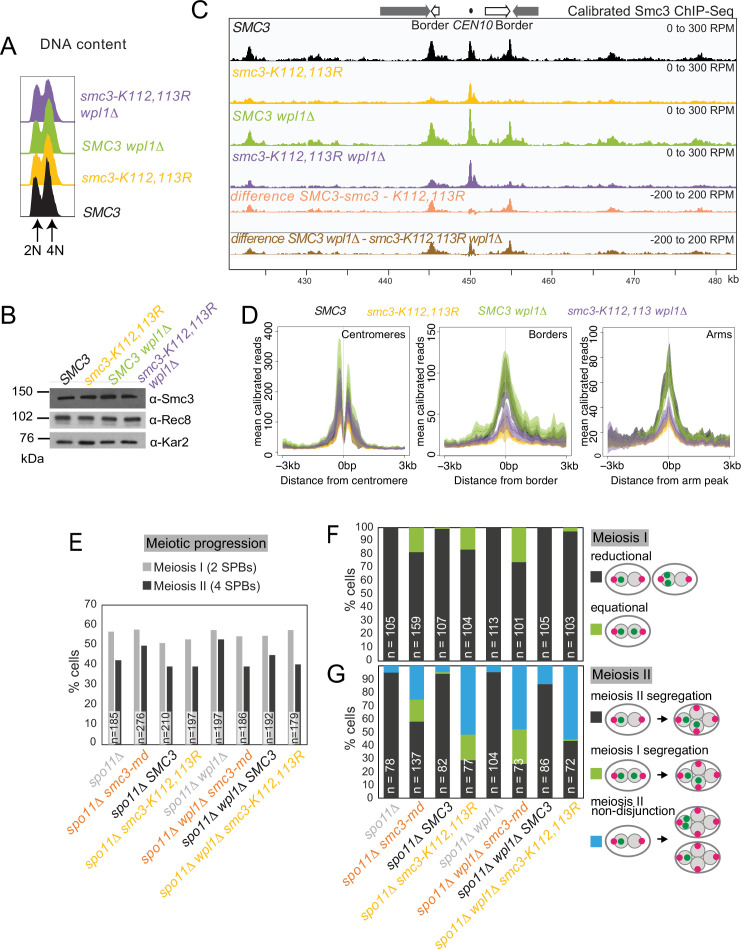
Figure 9. Smc3 acetylation is essential for meiosis.
(A–D) smc3-K112,113R leads to a global reduction in chromosomal Smc3 levels, which is only partially restored by WPL1 deletion. SMC3 (AM29315), smc3-K112,113R (AM29316), SMC3 wpl1Δ (AM30310), and smc3-K112,113R wpl1Δ (AM30311) strains carrying ndt80Δ were harvested 6 hr after induction of sporulation. (A) Flow cytometry profiles show similar DNA content at harvesting in all cultures. (B) Western immunoblot with Kar2 loading control (α-Kar2) shows comparable Smc3 (α-Smc3) and Rec8 (α-Rec8) levels in all cultures at the time of harvesting. (C) Calibrated Smc3 ChIP-seq for a representative region surrounding CEN10. (D) Mean calibrated ChIP-seq reads (line), standard error (dark shading), and 95% confidence interval (light shading) at all 16 centromeres, 32 borders, and 32 flanking arm sites. (E–G) Smc3-Ac is required to ensure co-segregation of sister chromatids in meiosis I and accurate meiosis II chromosome segregation. Meiotic progression (E) and meiosis I (F) and II (G) chromosome segregation were scored after live-cell imaging as in Figure 6 (B–E). Strains used were spo11Δ (AM30238), spo11Δ smc3-md (AM30240), spo11Δ SMC3 (AM30242), spo11 smc3-K112,113R (AM30244), spo11Δ wpl1Δ (AM30234), spo11Δ wpl1Δ smc3-md (AM30235), spo11Δ wpl1Δ SMC3 (AM30655), and spo11Δ wpl1Δ smc3-K112,113R (AM30237).