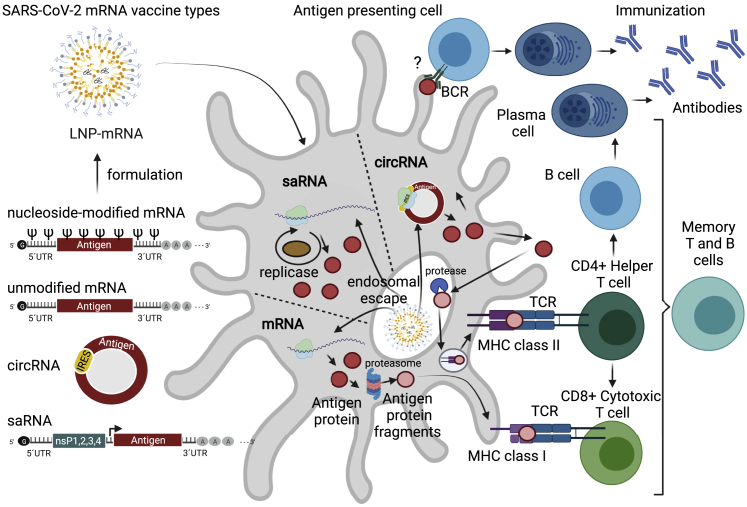
Figure 1.
Immunization against COVID-19 with mRNA vaccines
Immunization with mRNA vaccines requires an antigen-encoding mRNA transcript. The linear non-replicating mRNAs consist of a sequence encoding an antigen (e.g., the S protein for SARS-CoV-2) flanked by 5′ and 3′ UTRs, with a cap structure at the 5′ end and a poly(A) tail at the 3′ end.57 Depending on the use of native or modified nucleosides during IVT, unmodified or modified mRNAs are produced. saRNA consists of the same sequence organization, but in addition contains: (1) a sequence encoding four non-structural proteins (nsP1–4), which form a replicase responsible for amplification of the saRNA, and (2) a subgenomic promoter (black arrow) of viral origin that initiates transcription of antigens.50 circRNA for vaccine application consists of a covalently closed single-stranded RNA that contains antigen sequence and an IRES that allows initiation of antigen translation.49,59,60 Antigen-encoding mRNAs are formulated into LNPs, endocytosed, and released through the process of endosomal escape to the cytoplasm. The S protein is produced by the translational machinery of the APCs (red circles), degraded by proteasomes (pink circles), and presented on MHC class I (pink circles), leading to a specific CD8+ cytotoxic T cell response against SARS-CoV-2. Antigens can also be anchored to the membrane of the APC and directly recognized by BCRs leading to B cell responses; however, such a path and its contribution to antibody production is currently under debate. Finally, the antigen protein can be exported from the cell and endocytosed back to the same or another APC, degraded by endosomal proteases, and presented on MHC II structures resulting in a CD4+ helper T cell response. Immunization progresses with CD4+ helper T cells further helping in (1) activation of B cells that produce SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies and (2) activation of CD8+ cytotoxic T cells that may specifically recognize and eliminate virus-infected cells. APC, antigen-presenting cell; BCR, B cell receptor; circRNA, circular ribonucleic acid; IRES, internal ribosome entry site; IVT, in vitro translation; LNP, lipid nanoparticle; MHC, major histocompatibility complex; mRNA, messenger ribonucleic acid; saRNA, self-amplifying ribonucleic acid; SARS-CoV-2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; S protein, spike protein; TCR, T cell receptor; UTR, untranslated region. Figure was created with BioRender.com.