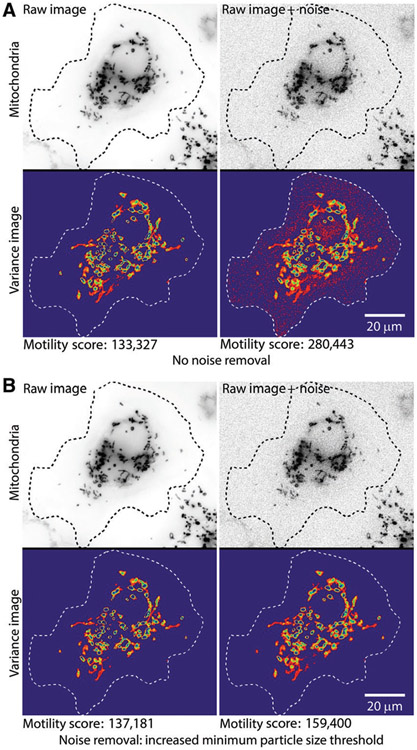
Figure 4.
Impact of pixel noise and demonstration of noise removal during step 1 of QuoVadoPro. To demonstrate the effect of pixel noise on quantification by QuoVadoPro, artificial noise is introduced in the sample cell with fluorescent mitochondria (previously shown in Figures 1 and 2). When the noise in the images is not filtered out, the noise pixels are retained in the 2D motility heatmap and significantly affect the motility score (A). However, when the noise pixels are filtered out, the impact of noise is greatly reduced or eliminated (B). QuoVadoPro gives the user multiple tools to remove image noise during its operation in step 1. In this example, one such tool is used, wherein a minimum size threshold can be declared for all discrete objects in the image. Any object below the minimum size threshold is eliminated. Because most image noise is in the form of isolated pixels, the user can choose a minimum size threshold of a few pixels (typically <3 pixels), to remove most of the noise.