Figure 4. Examples of sensory terminals involved in interoception.
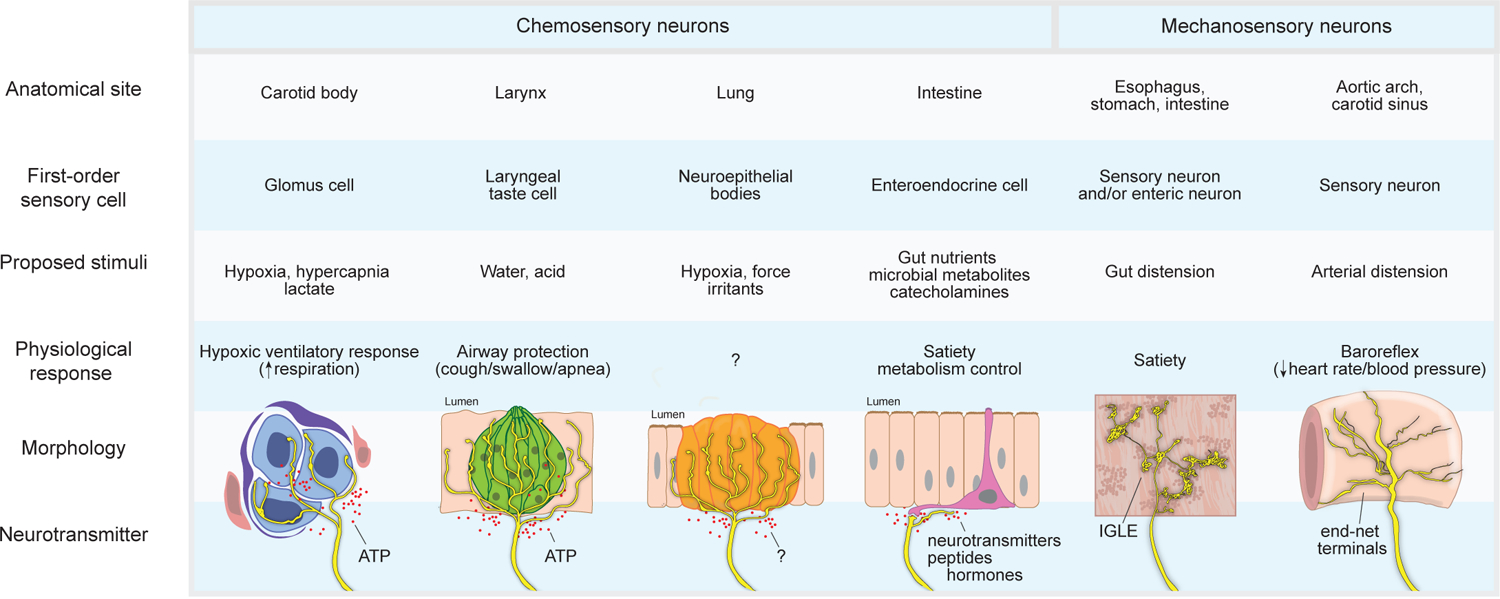
Vagal and glossopharyngeal sensory neurons include second-order chemosensory neurons that receive inputs from upstream sentinel cells, including glomus cells, taste cells, neuroepithelial bodies, and enteroendocrine cells, as well as mechanosensory neurons that form IGLEs and end-net endings. Various neuron types project to different organs, directly or indirectly detect different stimuli, display different terminal morphologies, and evoke different physiological responses.
