Fig. 3. Secondary metabolites as interspecies modulators of antibiotic resilience.
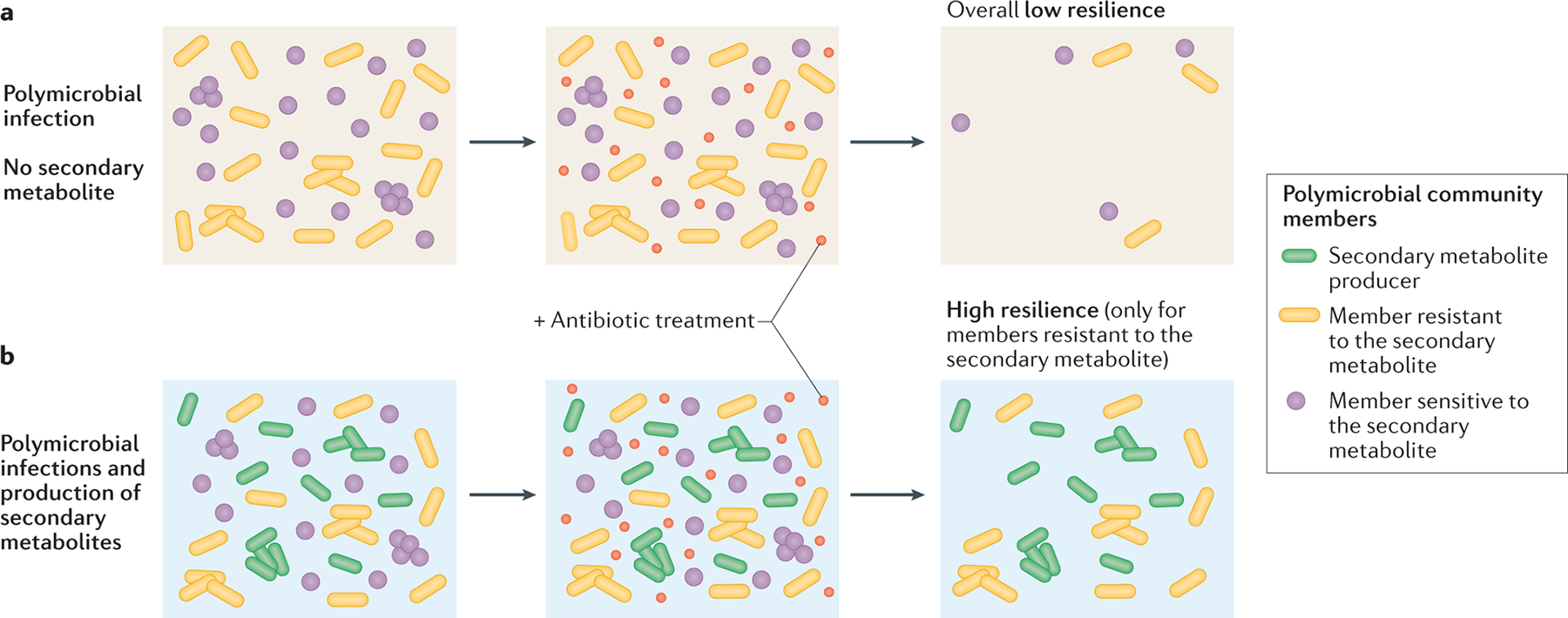
The presence of secondary metabolite producers in polymicrobial infections can alter the community susceptibility profile to antibiotic treatment. When the producer is not present (part a), overall resilience levels upon antibiotic treatment are low. However, through the secretion of the secondary metabolite, the producer’s presence (part b; green cells) can have distinct effects on different community members. For members intrinsically resistant to the secondary metabolite (yellow cells), the molecule’s presence can increase resilience to antibiotic treatment. However, if a member is sensitive to the secondary metabolite (purple cells), the added toxicity can overwhelm cellular defenses, potentiating the killing by the clinical drug.
