Fig 3. Cpx forms pores and remodels GUV membranes.
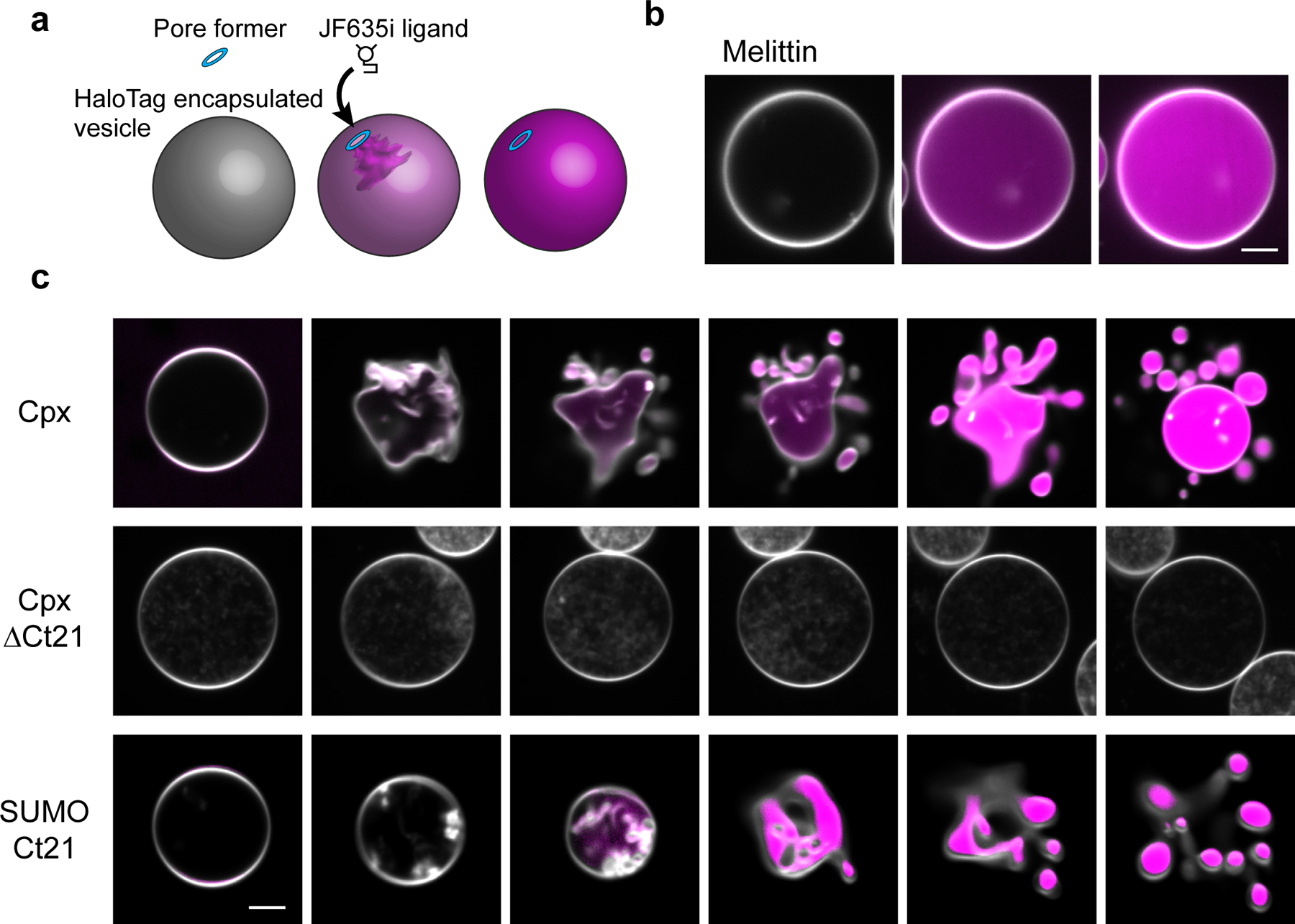
(a) Illustration of the GUV-pore formation assay. Recombinant HaloTag protein is encapsulated in the GUVs and the JF635i ligand is present in the media. Pore formation allows the ligand to enter the GUVs and bind the HaloTag protein, causing an increase in JF635i fluorescence (magenta). (b) Representative example of the GUV pore formation assay using melittin. GUV lipids are labeled with 0.1 % rhodamine-PE (white). Scale bar = 5 μm. (c) Progressive 5 second image series of GUVs after treatment of 5 μM Cpx, Cpx ΔCt21 or SUMO domain with the Cpx C-terminal helix, SUMO-Ct21. Pore formation and vesiculation was consistently observed in >10 repeated trials from >3 independent protein preparations. Scale bar = 5 μm.
