Table 1.
Overview of microbial macronutrient storage compounds with key references and characteristics.
| Storage compound | Occurrence | Structure | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Triacylglycerides (TAG) [139, 140] Hydrophobic lipids; as intracellular inclusions |
Widespread in bacteria and fungi, not in archaea | 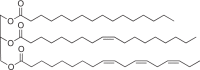 |
High energy density, but can only be mobilized for energy under aerobic conditions |
|
Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) [141, 142] High molecular-weight, hydrophobic lipid; as intracellular inclusions |
Bacteria and archaea, not in eukaryotes | 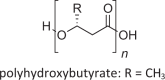 |
Intracellular PHA can comprise >80% of cell dry weight; can only be mobilized for energy under aerobic conditions |
|
Hydrophilic, high molecular-weight polymer of glucose; as intracellular granules |
Bacteria, fungi, animals, possibly archaea, not plants | 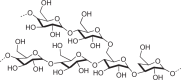 |
Polymer enables glucose storage without increasing osmotic pressure |
|
Nonreducing water-soluble glucose dimer |
Bacteria, archaea, fungi, plants, and invertebrates | 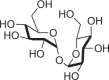 |
Plays roles in osmotic regulation and protection against desiccation |
|
Hydrophobic lipid; as intracellular inclusions |
Bacteria | 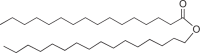 |
Also in eukaryotes, e.g., in hydrophobic leaf cuticles, but not as storage |
|
Storage of P and energy, as intracellular granules or in acidocalcisomes |
Ubiquitous, but extent of accumulation differs | 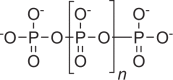 |
Multifunctional molecule also involved in pH buffering, heavy metal chelation, cell signaling, motility, and virulence |
|
Storage of N; as intracellular granules |
Cyanobacteria, some other bacteria | 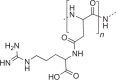 |
Up to 18% of cell dry mass of cyanobacteria and >40% in Acinetobacter calcoaceticus |
More details are provided in Supplementary Information 1.
