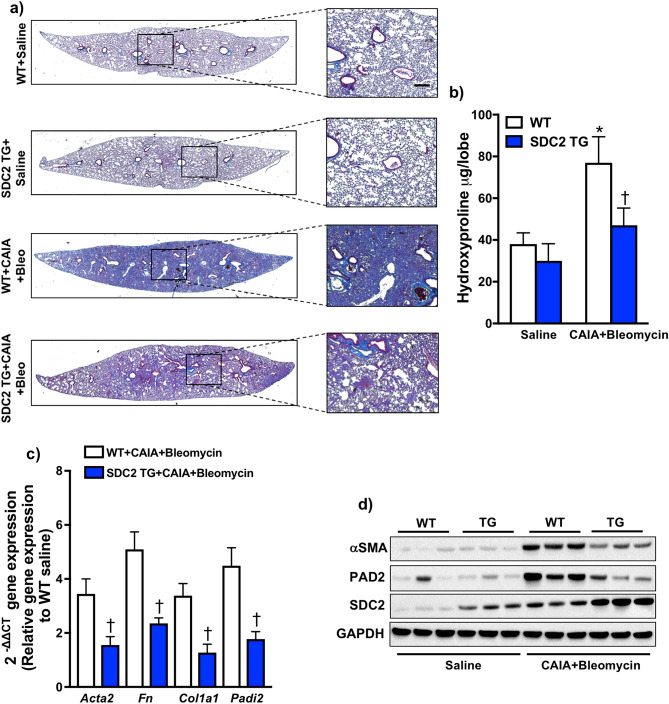
Figure 4.
Overexpression of syndecan-2 (SDC2) attenuates fibrosis in a mouse model of pulmonary fibrosis in the setting of inflammatory arthritis. Wild type (WT) and SDC2-transgenic mice (TG) were subjected to collagen antibody-induced arthritis (CAIA) followed by bleomycin (Bleo) injury or saline as described in the Methods. (A) 24 days later, mouse lungs were harvested and stained with Masson’s trichrome (n = 3 for saline and n = 5 for CAIA + Bleo groups). (B) Hydroxyproline content was measured in the left lung of WT (n = 12) and SDC2 TG mice (n = 12) exposed to CAIA + Bleo; and WT (n = 5) and SDC2 TG (n = 5) exposed to saline. (C) Gene expression of Fn and Col1a1, Acta2, Sdc2, and Padi2 in harvested lungs was measured using RT-PCR (n = 5 for each condition). (D) α-SMA, PAD2 and SDC2 levels were measured by Western blot. Data are mean ± SEM. P < 0.05; significant comparisons by one-way ANOVA: *vs. WT/saline, †vs. WT/CAIA + Bleo alone. Abbreviations: α-SMA = alpha-smooth muscle actin, Bleo = bleomycin, CAIA = collagen antibody-induced arthritis, GAPDH = glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase, PAD2 = peptidylarginine deiminase 2, SDC2 = syndecan-2, TG = transgenic, WT = wild-type.