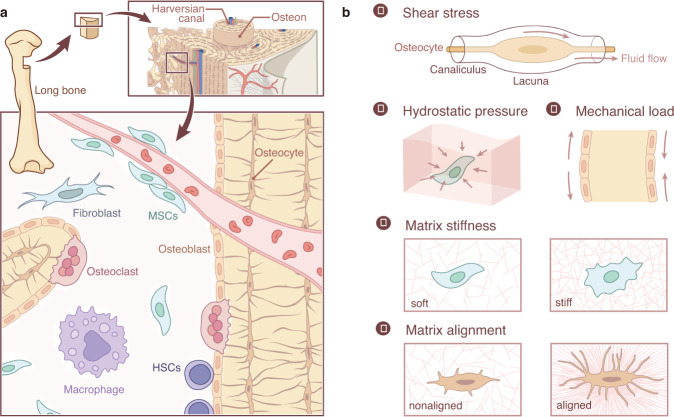
Fig. 1.
The structural basis of mechanical stress in skeletal cells. a The skeletal system contains osteoblasts, osteoclasts, osteocytes, and their progenitors, all sensitive to mechanical stimuli. Osteocytes are the most common mechanical sensors among these cells due to their structure and location in the bone matrix. Mesenchymal stem cells and osteoblast progenitors can sense the FSS in the bone marrow cavity and the strain on the bone. Osteoclasts are both mechanosensitive cells and the effectors for other mechanosensitive cells. b. The mechanical stimuli placed on bone may include shear stress, hydrostatic pressure, mechanical stretch and tension, matrix stiffness, and matrix alignment.