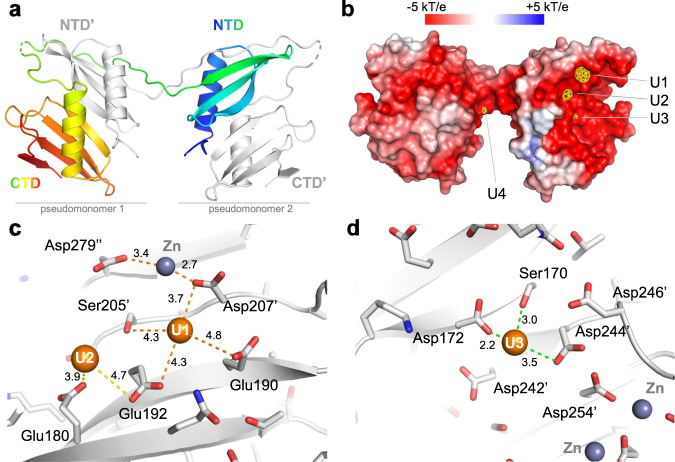
Fig. 3. Crystallographic structure of UipAext-ViU2A.
a An illustration of the dimer structure, with one monomer colored from the N-Terminus (blue) to the C-Terminus (red) and the second monomer colored in gray. b Molecular surface representation of the UipAext-ViU2A dimer (in the same orientation as in a) colored according to its electrostatic potential using the APBS plugin in pymol. The surface is superimposed with the anomalous map (yellow) collected at the uranium edge and contoured at 4σ all around the dimer. At this contour level, there are four uranium binding sites, three of which are localized on the negatively charged face of UipA (labeled U1-U3 as a function of peak height in the anomalous electron density map). c View of the two uranium binding sites U1 and U2. Ser205’ and Asp207’ indicate residues that are contributed by the second monomer of the domain-swapped dimer. d View of the third uranium binding site (U3). In (c and d), all of the residues are shown in stick form, and all distances from U atoms to residues located in a 5 Å radius are shown. The 2Fobs-Fcalc refined electron densities around the three uranium binding sites are shown in Fig. S37.