Fig. 4.
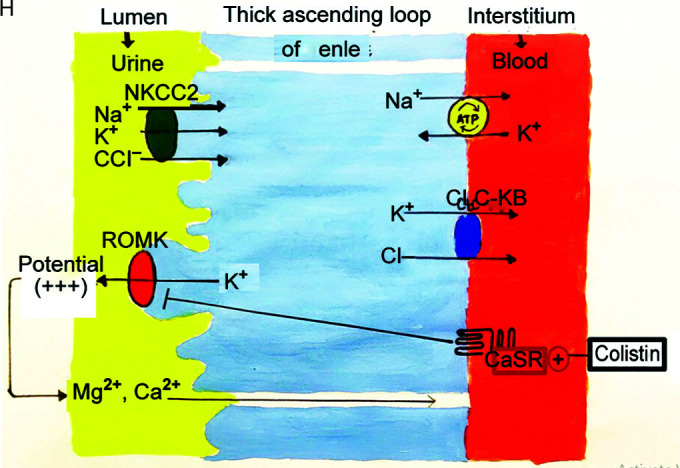
Reabsorption of sodium chloride is achieved with the help of sodium potassium 2 chloride cotransporter (NKCC2). For this channel to function, concentration gradient is required across the cell which is maintained by sodium pump (sodium-potassium adenosine triphosphates), chloride channel (ClC-kb) on basolateral side, and potassium channel on luminal side (ROMK). This apical potassium channel also maintains a relatively positive voltage potential on luminal side leading to paracellular reabsorption of Ca2+ and Mg2+. Based on defect on any of these channels BS has been classified into five types (Table 3). Type V is because of gain of function mutation in CaSR which normally inhibits the apical potassium channel. Gain of function leads to further inhibition of this channel, concentration gradient is lost, and thus leading to defective reabsorption of all the electrolytes. Colistin causes a similar defect in this calcium-sensing receptor
