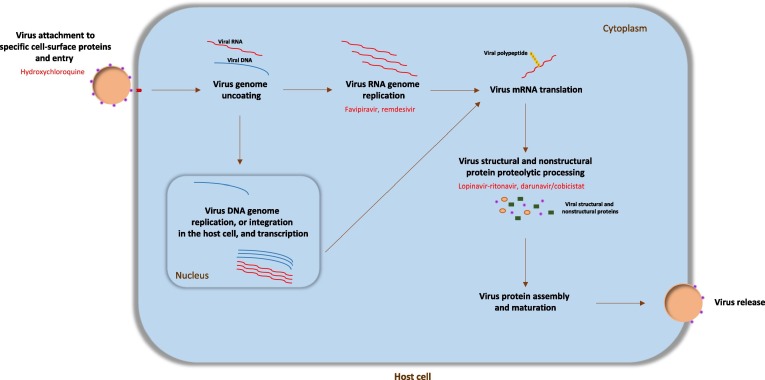
Figure 1.
The life cycle of viruses and antiviral drug targets. The virus initially binds to the host cell-specific receptors through its surface proteins, to allow internalization of the virus particle. The internalized virus releases its genome into the cell cytoplasm to be replicated (RNA in cytosol and DNA in nucleus), transcribed, and translated to produce viral proteins. Viral components are assembled to produce progeny virions, which are released out of the cell by budding or lysis of the host cell. Targetable stages of the virus life cycle are the endocytic entry of the virus into host cells; RNA/DNA replication and transcription; translation and proteolytic processing of viral proteins; virion assembly; and release of new virus particles through the exocytic systems. In red are shown the possible viral targets of some repurposed coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) drugs.