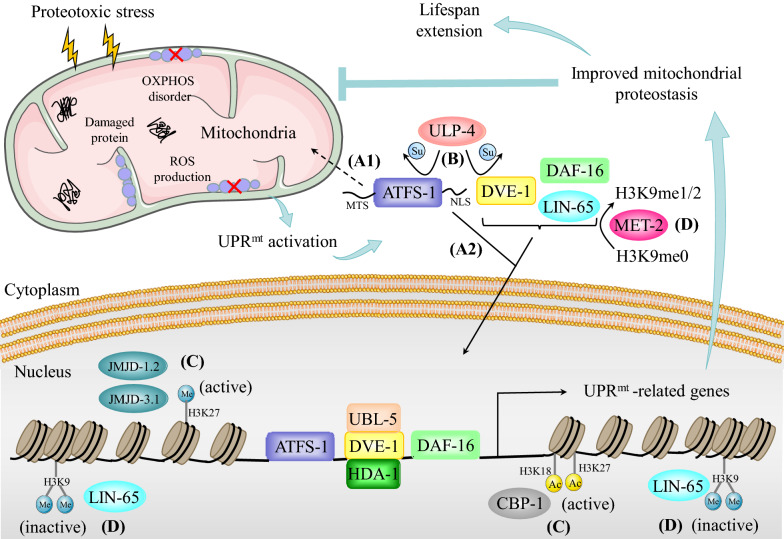
Fig. 1.
Mechanism of UPRmt in C. elegans. When mitochondrial proteostasis is disturbed, signaling molecules of UPRmt mediate mitochondria-to-nucleus retrograde communication. Transcription factors, including ATFS-1, DVE-1, and DAF-16, are activated by upstream signals and bind to the promoters of target genes, thus inducing the transcription of UPRmt-related genes. A1 Under nonstress conditions, ATFS-1 enters the mitochondria through the MTS and is subsequently degraded. A2 Under mitochondrial stress conditions, ATFS-1 is transported to the nucleus in an NLS-dependent manner. B ULP-4-mediated deSUMOylation of ATFS-1 and DVE-1 enhances ATFS-1- and DVE-1-dependent transcription programs. C JMJD-1.2-, JMJD-3.1- and CBP-1-dependent epigenetic modifications facilitate the formation of a nucleosome conformation that is conducive to transcription. D Additionally, MET-2- and LIN-65-mediated chromatin silencing of non-UPRmt gene regions is crucial for triggering UPRmt. Consequently, the activation of UPRmt promotes the recovery of mitochondria from damage, enhances mitochondrial function, and prolongs the lifespan of C. elegans